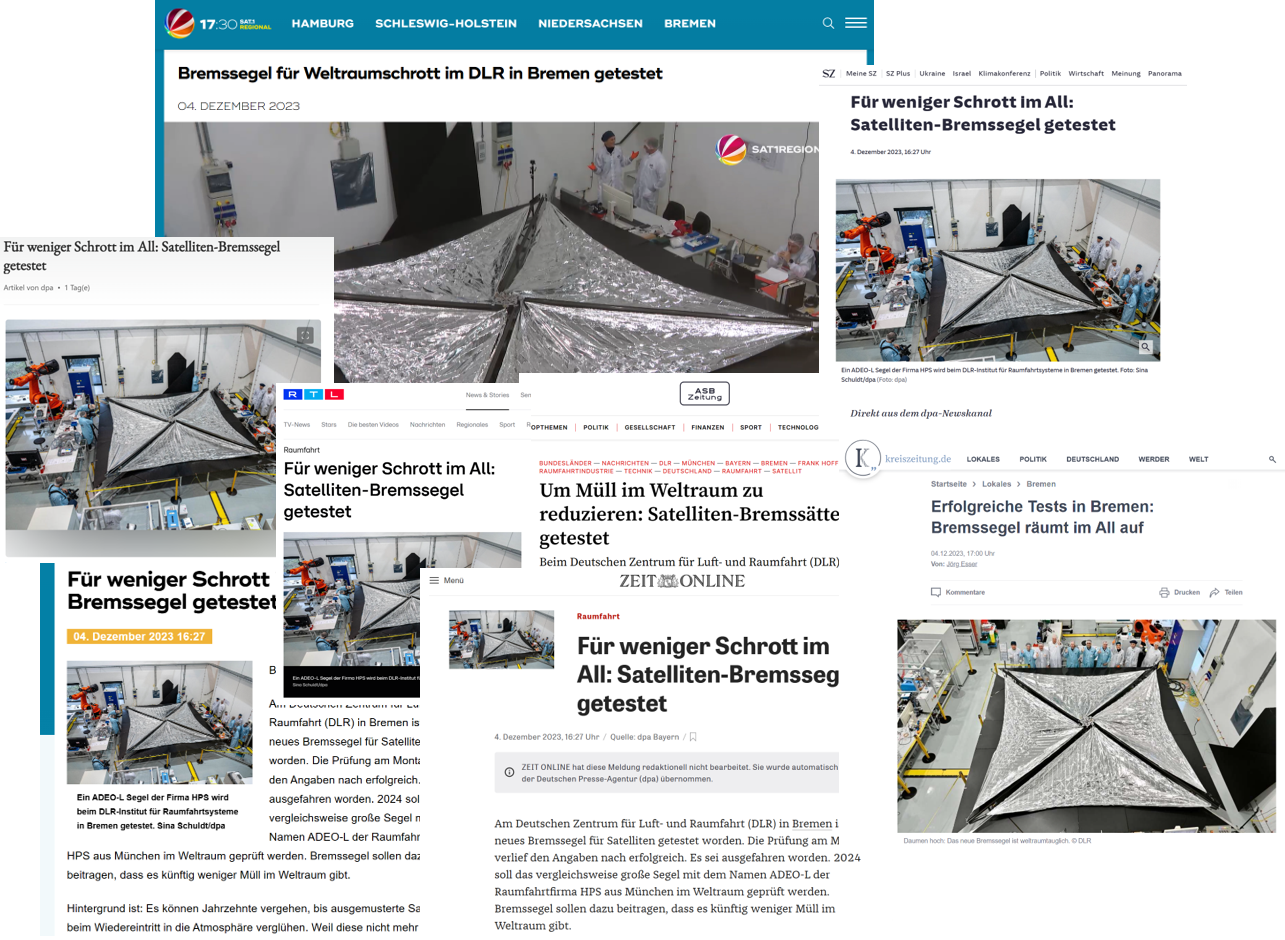
Dezember 2023
HPS Space News
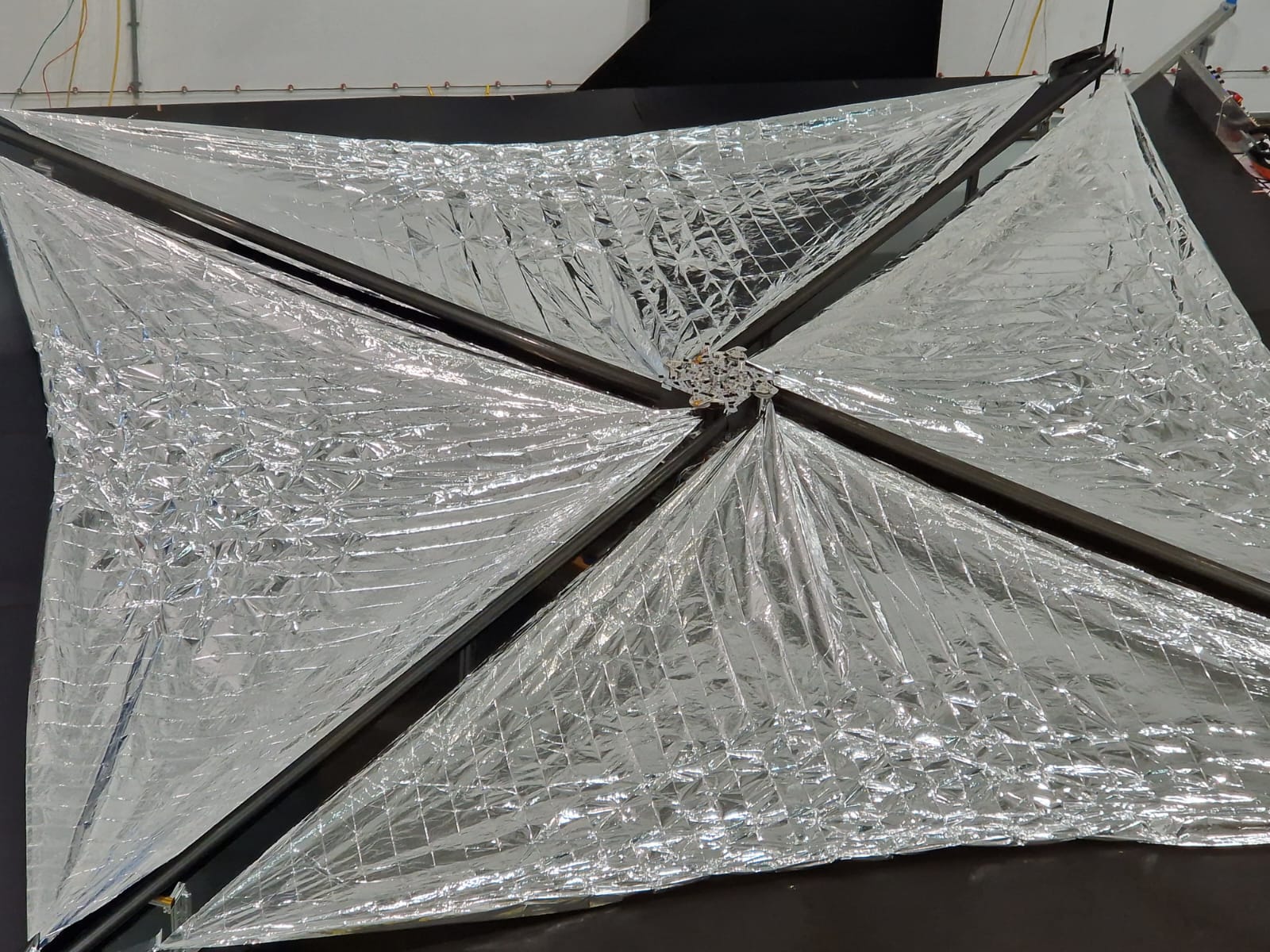
ADEO L1 “ready for lift-off”: World’s largest operational brake sail for the disposal of space debris successfully tested
ADEO L1 “ready for lift-off”: World’s largest operational brake sail for the disposal of space debris successfully tested
HPS completes the ADEO sail fleet with its first largest version under the version named L1. Its 25 square meters of sail area unfolded successfully deployed on Monday, 4th of December 2023 in a final ground test after a complete completed PFM qualification campaign. This included vibration tests in all axes as well as tests under thermal vacuum, including hot and cold firing tests (tests to verify the deployment release mechanisms under extreme temperatures). The tests were carried out under responsibility of HPS Munich at the facilities of the DLR Institute of Space Systems in Bremen – a prime example of cooperation between industry and research & development. This final and most important test enjoyed great interest from the media (including SAT1, RTL, NTV, DPA) covering the 20-minute deflation process and interviewing the enthusiastic project team of HPS and DLR. Links to the articles and television videos can be found HERE.
This test is also a success of ESA’s GSTP program, which significantly supported the development of ADEO-L1 financially and technically. Technology programs in general are essential for independent SMEs in the space industry and their products on the way to market readiness and worldwide series sales.
The ADEO brake sails deploy after the end of the satellite’s mission and brace themselves against the resistance of the atmosphere that still prevails in orbits up to an altitude of just under one thousand kilometers. This deployment immediately leads to a drastic reduction of the speed of the satellite and the entire package sets off on its accelerated descent towards the earth’s atmosphere, where it then burns up in the frictional heat of up to two thousand degrees Celsius. The entire return process takes even significantly less time than the latest guidelines prescribe. Until recently, the process could take up to twenty-five years, while it must now be completed within five years. And, to ensure that operators follow the rules, launch service providers such as SpaceX no longer even take satellites into space if they are not equipped with the appropriate return technology from the outset.
The Munich-based space-tech company HPS had this development in mind more than ten years ago, when no one else was really thinking about ways to avoid space debris. With great support from the space agencies ESA and DLR, the DLR institutes in Bremen and Braunschweig, the companies DSI, Bremen, and formerly HTS, Coswig, plus a seven-digit-investment of HPS, the company´s highly committed young team of experts has created an entire product family under the generic name ADEO, from the smallest versions ADEO-P (Pico), ADEO-C (Cube) and ADEO-N(Nano), ADEO-M (Medium) and the latest member of the group, ADEO-L (Large). The development master plan not only extends even further to possible ADEO variants with up to 100 square meters of braking surface, but also leaves enough room for derivatives with completely different applications, such as the monitoring of space debris smaller than1 cm directly in space.
In its largest flight-ready version to date, L1, ADEO has a take-off weight of 10 kg at dimensions of 43 cm x 43 cm x 25 cm; in contrast to the smaller versions, this unit also requires its own power supply for motor-controlled deployment of the masts and sails. ADEO-L1 generally fits perfectly on satellites up to the 1,500 kilo class.
In the first quarter of next year, ADEO-L1 will be integrated onto a satellite of the Belgian company Redwire for its first test flight at the end of 2024/beginning of 2025 as part of a EU program, while the versions ADEO-N1 and ADEO-N2 have already passed their baptism of fire in space. Approaching the fiery finale is currently ADEO-N2, deployed in December 2022. Since then, it has already lowered its satellite from an orbital altitude of 510 km to 460 kilometers in only 12 months without the aid of any fuel or attitude control. Expected “arrival” in a completely burnt-up state: mid2025 – and thus even around five times faster than without sails and twice as fast as prescribed.
ADEO-L1 will master this path of final in-orbit verification just as safely, company boss Dr.-Ing. Ernst K. Pfeiffer is certain. As with the other versions, it will then go straight into series production for which the company has special production facilities at its Munich and Bucharest sites.
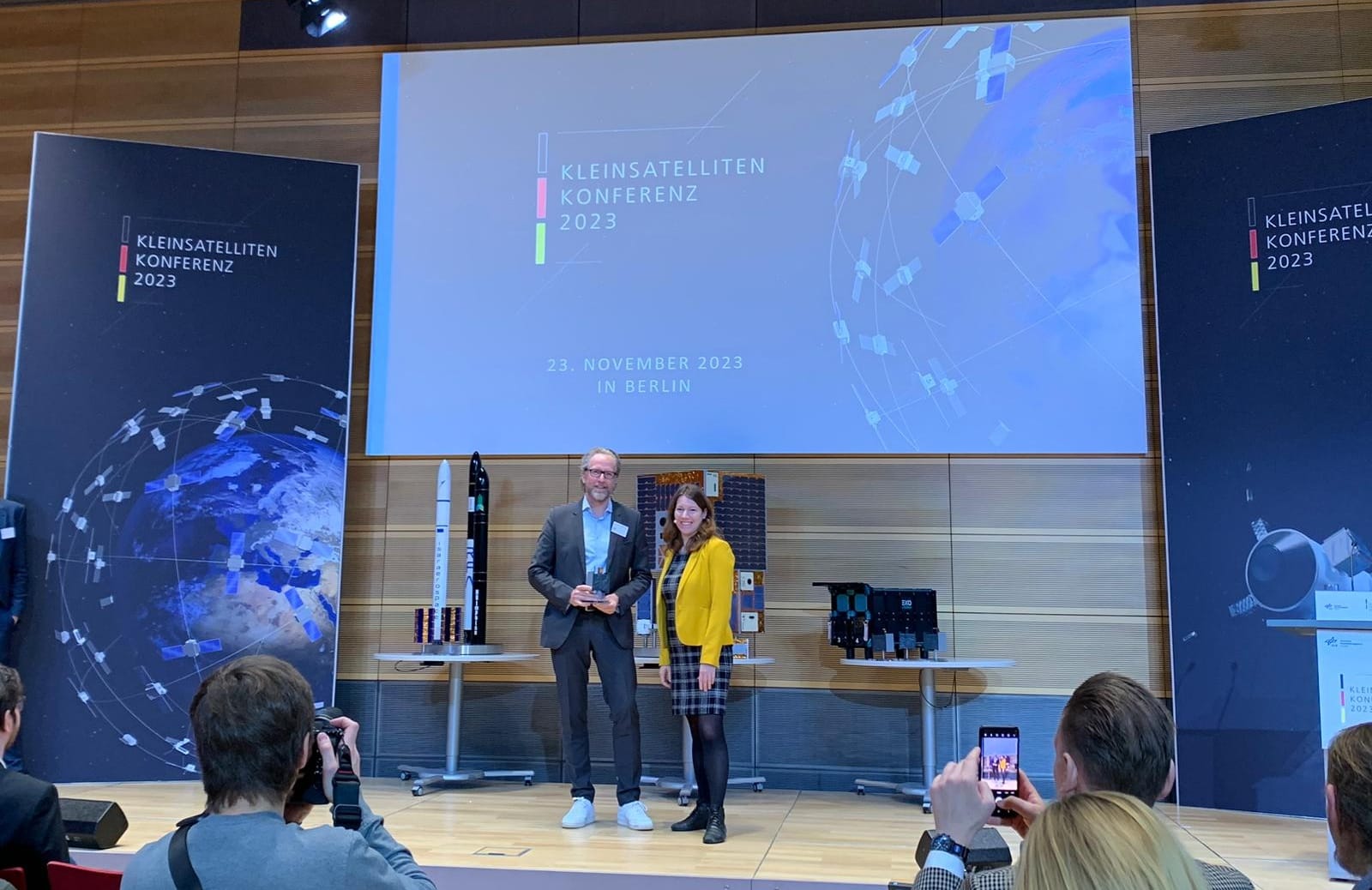
HPS wins German government space competition with ADEO deorbit sail
November 2023
Space sails from the ADEO series enable legal launch and disposal of satellites
As part of the National Program for Space and Innovation and based on the decision of the Budget Committee in November 2022, the German Space Agency launched a competition for promising space innovations. The winner can expect a fully organized and financed demonstration flight with launch by 31.12.2025. On Thursday, 23 November 2023, the Federal Government’s Space Coordinator, Dr Anna Christmann, selected Munich-based space technology company HPS as the winner of the competition in the small satellite payload category with its ADEO-Cube space sail version at the 2023 Small Satellite Conference. The ADEO product family is designed as a series with different model types (Pico, Cube, Nano, Medium, Large), with which all satellites from the Cubesats to the larger representatives with 1.5 tons (class “M”) are automatically removed from low Earth orbit (LEO) and disposed of at the end of the mission. This so-called “deorbiting” with the ADEO braking sail not only fulfills, but even undercuts the maximum duration of 5 years that will apply from October 2024 instead of the 25-year guideline that has been in place since the 1960s. Quite simply, this means that no satellite will soon be accepted for launch without special on-board technology, such as the appropriate space sail from HPS’s ADEO series, if it cannot otherwise be legally disposed of. Since SpaceX, for example, as the leading launch service provider, will be introducing this rule from October 2024, it will apply to practically all future satellites, including those that are already in the design and manufacturing phase today.
As HPS CEO Ernst K.Pfeiffer, there is still only one alternative to ADEO, but it “is chemical, expensive and – in the case of a damaged satellite – inoperable”, the passionate aerospace engineer states about the market position of the ADEO space sail: “ADEO is currently the cheapest, most reliable and cleanest solution for legal deorbiting on the global market, available in all classes thanks to series production at HPS Bucharest and HPS Munich, and highly competitive in the hotly contested commercial market for satellite technology.We at HPS, especially our development team, are all very pleased that our sustainable technology has been recognized by the Small Satellite Competition at the highest level.”

ESA´s “Zero Debris Charter” finalized – HPS among the first to sign
November 2023
ESA´s “Zero Debris Charter” finalized – HPS among the first to sign
Initiated by ESA´s office for “Strategy and Transformation” a considerable group of European space companies, including HPS, got together in order to jointly draft and now implement this continent´s set of rules for sustainable use of space. HPS is one of the first companies to sign the document on November 7th, 2023. Though legally non-binding, the “Zero Debris Charter” aims at putting an end to the inconsiderate and irresponsible pollution of space with tech-junk. In detail, the Charter clearly names the following targets:
- The probability of space debris generation through collisions and break-ups should remain below 1 in 1,000 per object during the entire orbital lifetime. A suitable aggregate probability threshold for constellations of satellites in the low Earth orbit region should be identified.
- Timely clearance of low Earth orbit and geostationary Earth orbit regions should be achieved with a probability of success of at least 99% after end of mission, including through external means when necessary.
- The casualty risk from re-entering objects should remain significantly lower than 1 in 10,000, striving towards zero casualty. A suitable aggregate risk threshold for constellations of satellites in the low Earth orbit region should be identified.
- Routine and transparent information sharing should be facilitated and active participation in strengthening global space traffic coordination mechanisms should be encouraged.
- Access to timely and accurate data on space objects down to a size of 5 cm or smaller in low Earth orbit and 20 cm or smaller in geostationary Earth orbit should be improved to enhance decision making capabilities for collision avoidance.*
Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS at the signature ceremony: “In our days now space is rapidly developing into the most important resource for the implementation of new technologies shaping our future on Earth. All efforts to preserve space from the beginning are therefore nothing less than efforts to preserve the fundamental conditions of life and its prosperity for humankind´s generations to come.”
*For more see:
*https://esoc.esa.int/zero-debris-community-update
*https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Clean_Space/World-first_Zero_Debris_Charter_goes_live
*https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Clean_Space/ESA_s_Zero_Debris_approach
*https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Clean_Space/The_Zero_Debris_Charter
HPS presents ADEO space deorbit-sail, the world’s only product series of its kind for the legal disposal of disused satellites
November 2023
SpaceTech Expo Bremen: HPS presents the ADEO space deorbit-sail, the world’s only product series of its kind for the legal disposal of disused satellites
Less than 36 months ago, they were regarded by many as nothing more than political empty phrases: the “Green Deal” of the EU Commission in Brussels and the “National Orbital Debris Implementation Plan” of the White House in Washington. Satellites continued to be launched into near- and far-Earth orbits with the prospect of becoming junk and endangering other missions for a quarter of a century after they finally burned up in the atmosphere. But that’s over now: With the adoption of the “Zero Debris Charter”, ESA has committed itself on November 7, 2023 to taking steps towards total avoidance of any space debris from 2030 at the latest, and even more concretely, namely already from October 2024, SpaceX, with over one hundred launches per year the world’s most important launch service, will no longer transport any payloads that are not equipped for their disposal within a maximum of 5 years after the end of mission operations. And as early as 2023, the U.S. FCC (“Federal Communications Commission”), as the supervisory authority for the allocation of radio frequencies, sentenced a satellite operator to a fine of $150,000 for prolonging the operation of his satellite with the propellant actually reserved for disposal, thus recklessly endangering all other missions in the vicinity. While the sum might make some people smile, the FCC has now put an end to all symbolism with its decision to no longer grant radio licenses to satellites without on-board technology for return (technical term: “deorbit”) within 5 years of the end of operations. Under the double threat of operation AND launch ban, practically all operators are forced to equip new satellites only with guaranteed reliable deorbit technology from now on.
This can be done with the on-board propulsion system using chemical propellants while shortening mission and profit, but even that does not work in case of satellite failure and is also comparatively expensive due to the need for constant control monitoring from the ground.
The alternative is called ADEO: from HPS (Munich and Bukarest) a space sail, self-deploying at the end of the mission, which automatically removes the satellite from space well below the specified deorbit times, is ideally suited as baseline-tech and emergency parachute. Already 36 million flight kilometers before the planned maneuver, the German specialist for orbit guidance and collision avoidance OKAPI:Orbits (Braunschweig) as a cooperation partner calculates the point for the descent without risk for other satellites. In addition, HPS partner number two, the Italian company AVIOSONIC, in constant liaison with the worldwide air traffic control stations, ensures via new ADEO-features highly accurate position conrol and spares aircrafts from hits by any satellite parts that may not have burned up.
The ADEO product family with officially attributed highest possible level of reliability (“TRL 9”) holds tailor-made solutions for all satellites from the tiny Pico- and Cube-Sat up to the 1.5 tonner and for all low-Earth orbits up to a distance of 900 kilometers from Earth. All ADEO lines are mass-produced by HPS, yet they feature adaptive design for special requirements that may arise from satellite design.
The prices of all ADEO models without exception are considerably lower than the expenditures required for deorbiting with chemically driven engines – apart from the fact that the safety of the deorbit of even these satellites – for example in the event of a system failure – can actually only be guaranteed by an ADEO system carried along as a backup.
For more detailed information on ADEO see: https://www.hps-gmbh.com/en/portfolio/adeo-angel-on-wings/
Raumfahrtpolitik: Die Ampel steht auf Rot für strategische Positionierung und Mittelstand (Ein Kommentar)
September 2023
Space policy: The lights are red for strategic positioning and SMEs. (A commentary)
Erster September – der Herbst steht vor der Tür. Fallen werden bald die Blätter, so wie jedes Jahr. Fallen werden auch Entscheidungen, wie etwa über den nächsten Bundeshaushalt – ebenfalls wie jedes Jahr. Zum ersten Mal aber in der Geschichte der Raumfahrtpolitik drohen diese Budgetentscheidungen besonders jene Teile der Raumfahrtindustrie zu Fall zu bringen, als deren weiße Ritter sich die verantwortlichen Politiker in der Öffentlichkeit aller Wirklichkeit zum Trotz unverdrossen weiter präsentieren: Raumfahrt zum Schutz für die Erde und zum Nutzen der Menschen, wirtschaftliche Stärkung von Innovation durch den Mittelstand, Euphorie bei der Neugründung von Startups und nicht zuletzt den strategischen Wunsch Deutschland als starken Partner in der Weltwirtschaft und -politik zu behaupten.
Für diese Ziele schaltet die Ampel in Berlin aber nicht nur allein durch geplante Budgetkürzungen auf Rot: Mit den schon im April für die Diskussion im Herbst aufgemalten Eckpunkten einer neuen deutschen Raumfahrtstrategie, über die ebenfalls im Herbst beschieden werden soll, deutet sich unumkehrbar ein negativer Paradigmenwechsel in der Wirtschaftspolitik zur Raumfahrt an: da, wo „Resilienz“ gefordert wird, mit fliegenden Fahnen hin zur Großindustrie, da, wo „Exzellenz“ gezeigt werden soll, hin zur weiteren Stärkung der Staatsinstitutionen, dort, wo „Souveränität“ gefragt ist, im Eilschritt hin zum Fortdelegieren von Zielsetzung und Programmführung unter den Rocksaum der mächtigen EU. Und die deutsche Raumfahrt profitiert von noch mehr Engagement der Politik: Die für jede politische Sonntagsrede ach so wichtigen Startups erhalten kostenlosen Nachhilfeunterricht im Umgang mit der Bürokratie und ihren Antragsformularen, die Forschungslandschaft wird effektiver durch bessere Vernetzung, und KMU, die Kraft aus der Mitte? Sie erhalten Unterstützung auf neuem Niveau – moralisch. Oder wie sollte sonst eine Budgetkürzung bei einer weltweit anerkannten Zukunftstechnologie und -fähigkeit (z.B. die Beteiligung an Infrastrukturthemen wie für eine europäische satellitengestützte Kommunikation IRIS²) mit einer Neuauflage einer Raumfahrtstrategie zusammenpassen?
Offenbar sollen also nun beide Handlungsstränge, das Kürzen des Raumfahrtbudgets und die neue, ausdrücklich für jedwedes Budget passende Raumfahrtstrategie harmonisch bei der Gestaltung der künftigen Raumfahrt-Wirtschaftspolitik zusammenwirken. Das Ganze so gekonnt formuliert, dass der flüchtige Leser meinen könnte, es ginge voraus in die helle Zukunft und nicht zurück ins dunkle Mittelalter der Raumfahrtpolitik.
Noch ist es nicht so weit, und damit es auch nicht so weit kommt, hat Ernst K. Pfeiffer in seiner Funktion als Sprecher des Raumfahrt-Mittelstandes (AKRK und Best of Space) zusammen mit deren Mitgliedern noch im Juli einen offenen Brandbrief im Namen der engagierten deutschen Raumfahrt-KMU und Startups direkt an den Bundeskanzler Olaf Scholz geschrieben und zudem das Angebot von Finanzminister Christian Lindner zum Dialog im August angenommen, um auf die drohenden Gefahren wirtschaftlicher und strategischer Verluste hinzuweisen.
Three months from Kick-off until the breadboard of the feed is tested
July 2023
Three months from Kick-off until the breadboard of the feed is tested
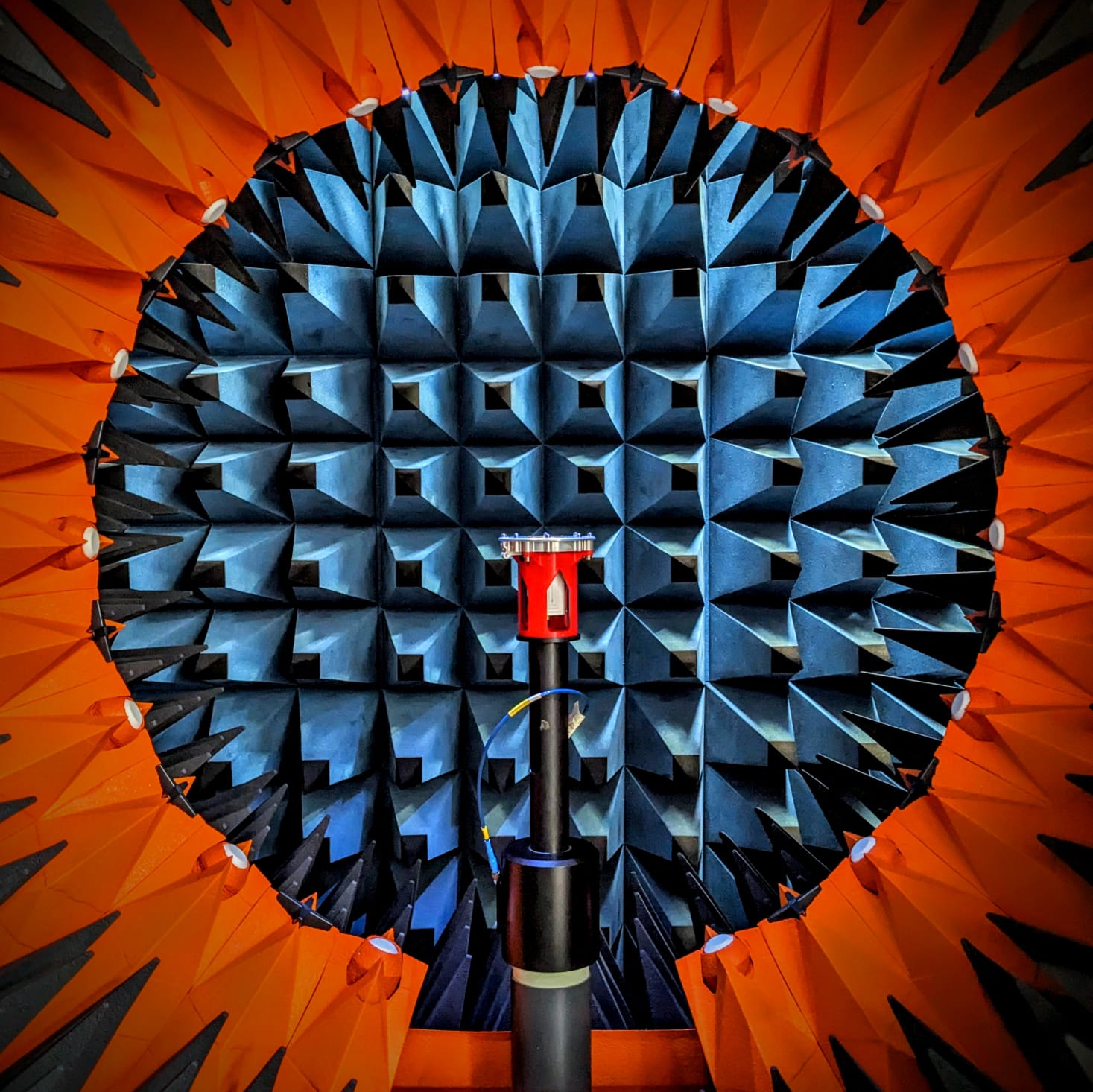
The picture shows our breadboard model of the feed developed by HPS for the BANT antenna during the RF test done at MVG Italy using the StarLab measurement system. The purpose of the test is to validate the feed design by comparing the RF simulations with the results of the measurement.
Adopting the New Space approach, it took only three months from the project Kick-off until the breadboard of the feed is tested. The flight model of the BANT antenna, where this feed will be installed, will be ready to be integrated on the spacecraft at the end of this year, the satellite will be then placed in Low Earth Orbit for a remote sensing mission.

July 2023
Antenna specialist HPS congratulates German Aerospace Center, DLR
With the perfect launch on 05.07.2023 of the last Ariane 5, the Heinrich Hertz mission has now begun. The technical ambitions of the project now depend crucially on the reliability of the invisible umbilical cord of the data transmission between sky and earth, satellite and ground station as on the #sidedeployable “H2NBA” (Heinrich Hertz North Beam Antenna) from the house of the German antenna specialist HPS.
The Ka-band antenna from HPS with reflector (completely made of CFRP), feed-chain & tower, “hold-down-and-release-” as well as “deployment- and pointing-mechanism“, is extremely lightweight and at the same time geometrically stable. It offers high Eigenfrequency and is not only suitable for the intended data transmission in the high-frequency Ka-band, but also for the even higher frequency band Q/V-band. On 09.07.2023 the HPS-Antenna has successfully been deployed, which is always one of the most critical steps of larger satellite antennas after launch. Now it means, the mission’s data transfer can start.
Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS: “We warmly congratulate DLR, the mission prime OHB, our direct customer TESAT (payload responsible) and all others involved in this ambitious project on the launch of the mission and the successful first steps in setting the satellite into operation. All of us at HPS are proud to have contributed our part to the central communications technology with the H2NBA sviveling antenna.”
The Heinrich Hertz Mission and its partners:
The Heinrich Hertz mission is the first time that a dedicated German communications satellite has been launched to research and test new technologies and communications scenarios. The mission is thus also making a contribution to the information society in Germany. The Heinrich Hertz mission is being led by the German Space Agency at the German Aerospace Center (DLR) in Bonn on behalf of the Federal Ministry of Economics and Climate Protection (BMWK) and with the participation of the Federal Ministry of Defense (BMVg). OHB-System AG was contracted to develop and build the satellite. Also involved in the development and testing of the satellite are the companies IABG GmbH, MDA AG and TESAT GmbH & Co. KG are also involved in the development and testing of the satellite. The ground segment with the control center in Bonn is being handled by OHB Digital Connect in conjunction with CGI. The sites for the new ground stations are located in Hürth (North Rhine-Westphalia) and Neustrelitz (Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania). Arianespace is responsible for launching the mission on board the Ariane 5 launcher (VA261). A total of 42 partners are involved in the mission – 14 of them on the scientific payload – one of them is HPS.
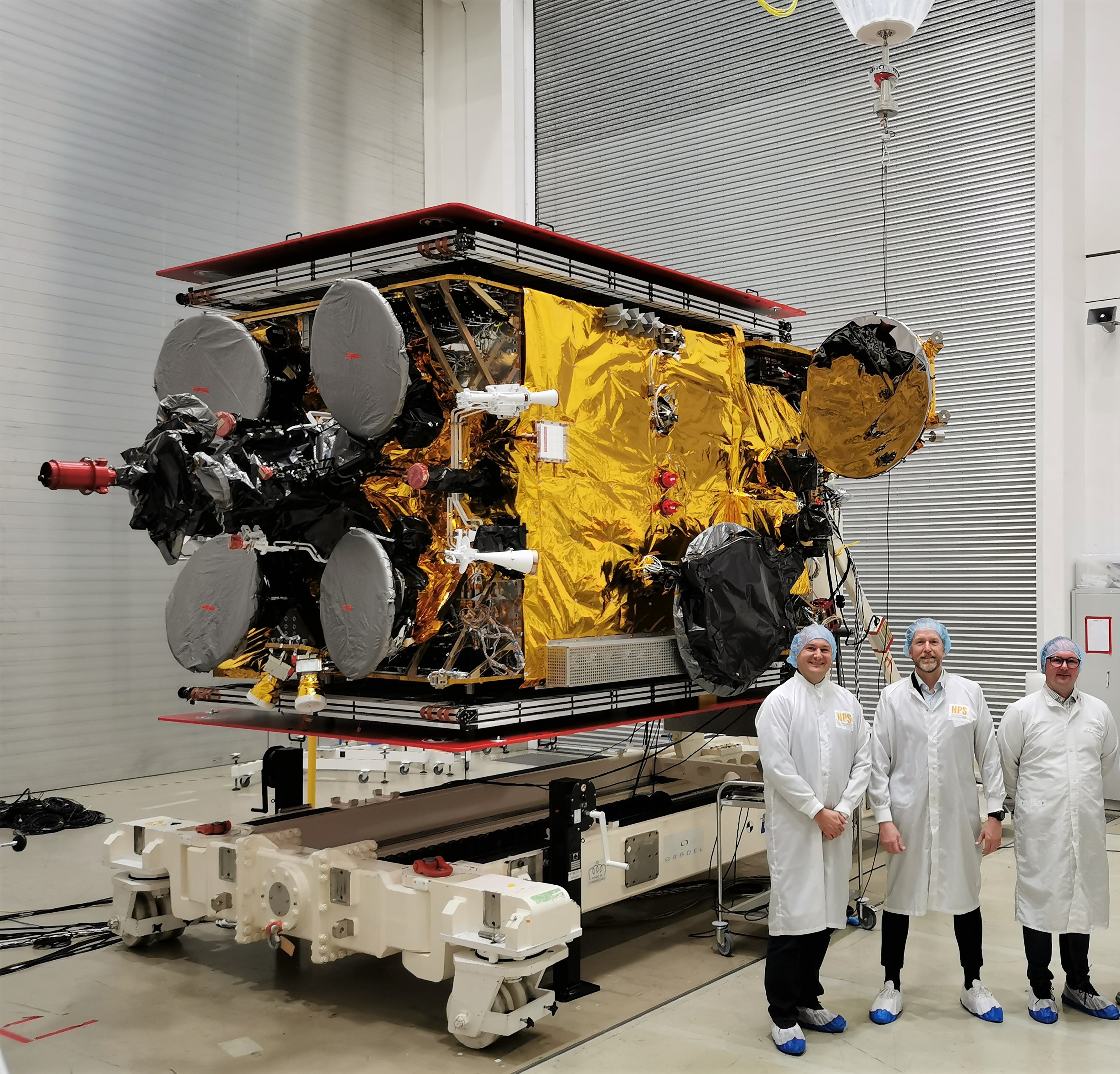

HPS congratulates ESA and TAS to the launch of EUCLID and to the successful checkout of the downlink antennan chain!
July 2023
State-of-the-art antenna to serve one of the most ambitious science missions ever
HPS, leading provider of advanced antenna- and reflector-technologies, applauds the ESA – European Space Agency and to the mission prime ThalesAleniaSpace (Italy) to the launch of space mission EUCLID (within European Space Agency’s Cosmic Vision Programme) on Saturday, 01.07.2023, which aims to unravel the mysteries of the dark universe and gain insights into the nature of „dark matter“ and „dark energy“. On Sunday, 09.07.2023 it has been confirmed that the „K-band signal has been received from EUCLID“ by the ground station on Earth.
Euclid is now the biggest transmitter of data (in terms of data rate of about 74 Mbps) from trans-lunar space: Read here the article from ESA
EUCLID´s “Antenna Reflector Assembly (ARA)” developed by HPS, together with its subcontractor Invent represents a significant advancement in space communication technology. Its innovative design and advanced features make it an ideal choice for the mission, enabling high-speed data transmission and reception from the spacecraft to Earth and back, bridging the distance of 1,5 Mio km. A deep “Thank You” for the trust into our team to our Customer Chain TAS (SP) – TAS (IT) – ESA, backed by our German Space Agency DLR.
Key features of the HPS ARA:
- Enhanced Signal Reception: The CFRP-based reflector’s high-gain capabilities, also under high temperature grades far away in L2-orbit, ensure optimal reception of the weak signals from the EUCLID spacecraft, enabling precise data collection on Earth from distant corners of the universe.
- High-Speed Data Transmission: Equipped with the reflector‘s state-of-the-art transmission CFRP material technology, the HPS-antenna facilitates rapid data transfer in K-band, allowing for real-time analysis and quick response to mission requirements.
- Robustness and Reliability: Designed to withstand the harsh conditions during launch and in space, the reflector assembly is built with durable materials.
- Compact and Lightweight: HPS` antenna design prioritizes accommodation efficiency without compromising its performance. Its compact size and lightweight construction optimize interface loads to the spacecraft and payload capacity.
“We are thrilled to contribute significantly to the EUCLID mission with our advanced reflector assembly,” says Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS. “Our cutting-edge CFRP-technology, developed for more than 15 years, can now play a crucial role in facilitating seamless communication between the spacecraft and ground stations, allowing the investigation of dark material by huge amount of data downloaded to Earth.”
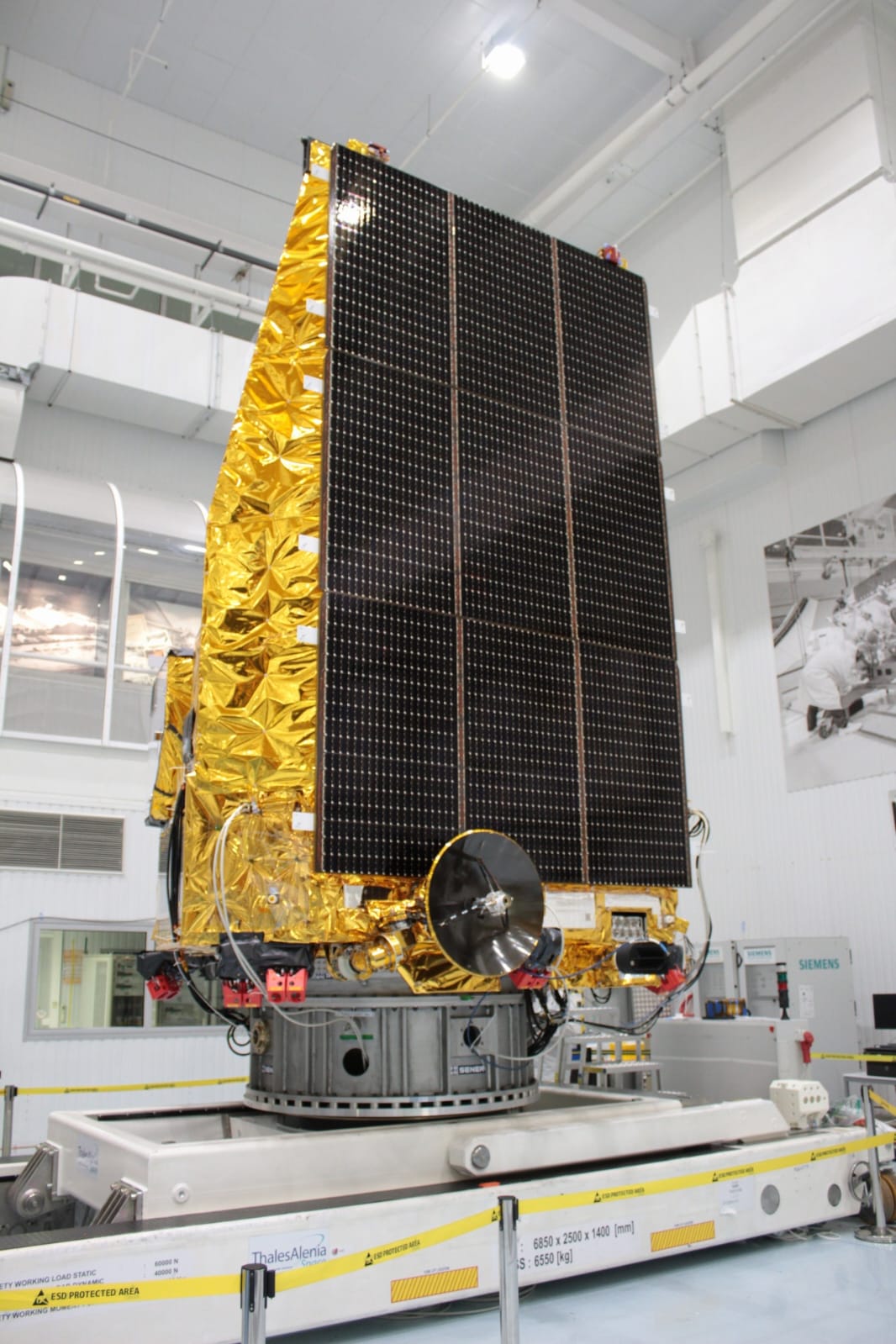

Picture by ESA
For the Sake of Safety and Sustainability in Space: OKAPI:Orbits´ AI now available as Assistance System to ADEO Deorbit Sail for Satellites
June 2023
Germany´s leading collision avoidance system reliably predicts the perfect slot for descent through tons of debris and space traffic.
When, after two, five or more years of operation, a satellite is supposed to leave its orbit and re-enter Earth, it’s a ride on the skyway to hell in two respects: first, for the satellite which is destined to burn up in the atmosphere, but also for other satellites as well as for an encounter with scrap parts that could hit it like unguided missiles – and produce even more junk. Satellites equipped with the ADEO braking sail from HPS are already in automatic descent mode. From now on, however, this can be upgraded by the Collision Avoidance system from industry-leading German startup OKAPI:Orbits. The company emerged as a spinoff from Braunschweig University of Technology in 2018 after over 40 years of intensive research. This Collision Avoidance System minimizes the collision risk during the de-orbit trajectory by figuring out the situation even ten days in advance. Appropriate maneuvers are also recommended for the satellite’s control system. This is made possible by the unique AI behind OKAPI:Orbits.
“Picture a distant view of 6.72 million kilometers of orbits on which about 10,000 satellites, 1,000,000 large and medium objects and 130,000,000 small ones exist that are not currently trackable. This is how complex computing operations is. Now, we should also take into account their velocity of 20,000 to 30,000 kilometers per hour. To any human sensibility, this is pure chaos, which the artificial intelligence behind our Collision Avoidance Software handles with aplomb,” says OKAPI’s company CEO Kristina Nikolaus.
Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS, a medium-sized innovation company, adds, “Our ADEO braking system not only performs the fastest possible passive descent even under adverse conditions – for example, when the satellite is already dead – it is also the deorbit solution with the largest safety reserve directly on board. Customers who don’t want to rely solely on their own software to control their satellites will find a unique safety architecture for the deorbit of almost all satellites with ADEO’s optional assistance systems for position tracking (Aviosonic) and optimal descent prediction (OKAPI:Orbits) at HPS.” ADEO is under discussion as a deorbit subsystem for the satellites of Europe’s coming constellation IRIS2 and “together with the features of Aviosonic and OKAPI:Orbits it levers the constellation to the most secure and sustainable one also after satellites’ nominal lifetime.”
During descent, the combination of all three technologies onboard the satellites will increase significantly the orbit determination and prediction, which is a unique advantage also for other satellites, constellations and stakeholders like owners, operators, and insurers.

HPS Joins Net Zero Space Initiative to Drive Sustainable Space-Tech Innovation
June 2023
HPS Joins Net Zero Space Initiative to Drive Sustainable Space-Tech Innovation
[Munich-Bucharest-Paris, June 12th, 2023] – HPS GmbH, a leading technology company specializing in cutting-edge solutions, is pleased to announce its membership in the Net Zero Space Initiative, an ambitious global movement dedicated to supporting sustainable practices and innovations in space.
The Net Zero Space Initiative brings together industry leaders, organizations, and experts from various sectors to collaborate on finding concrete solutions to combat space debris, thus preserving not only the economic and scientific benefits of outer space, but also its strategic potential in addressing urgent challenges such as climate change. By joining this esteemed network, HPS reaffirms its commitment to environmental stewardship and especially to a sustainable development of space infrastructures.
As a member of the Zero Space Initiative, HPS GmbH will actively contribute to the collective efforts aimed at developing sustainable technologies and practices across its operations. The company will leverage its expertise and its political as well as its industrial network to drive transformative change.
HPS drives advanced technology solutions like the world market leading deployable deorbit sail “ADEO” which enables quick decay of satellites until re-entry, reducing the risk of in-orbit collisions. By joining the Net Zero Space Initiative, the company aims to accelerate these efforts, collaborating with like-minded partners and leveraging collective knowledge to drive greater impact.
“We feel that as a part of the Net Zero Space Initiative we are with the right people,” said Dr. Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS. “At HPS, we believe that sustainability is both, a responsibility and an opportunity for innovation.
By collaborating with the Net Zero Space Initiative, we can amplify our efforts in developing and implementing sustainable solutions, contributing to a “greener” future in space and for our planet.”
As an advocate for sustainability, HPS GmbH Germany, as well as its affiliate HPS S.R.L. Romania, remain committed to driving positive change through its products, services, and operations. The company’s membership in the Net Zero Space Initiative represents a significant milestone in its sustainability journey.

HPS is Prepared to Provide ADEO Special Stealth Sail Edition for Europe´s IRIS2 Constellation Satellites
May 2023
HPS is Prepared to Provide ADEO Special Stealth Sail Edition for Europe´s IRIS² Constellation Satellites
The ever-growing number of satellites orbiting Earth presents a significant challenge in terms of space debris management. As space agencies and private companies deploy increasing numbers of satellites, finding effective and sustainable solutions for their safe disposal has become paramount. In this regard, the ADEO Deorbit Sail, developed by HPS offers a groundbreaking technology that enables controlled and efficient satellite deorbiting for mitigating space debris and ensuring long-term sustainability in space. By harnessing the natural forces present in space, such as solar radiation pressure and atmospheric drag, the sail facilitates controlled reentry of satellites into Earth’s atmosphere at the end of their operational life.
ADEO has already reached ESA´s hightest level of maturity, TRL 9 and proven its reliability on a number of spaceflights; getting ready to serve Europe´s new constellation IRIS2 its NewSpace-team at HPS, Munich, take it even one step further and introduce the ADEO special “stealth” sail edition. While irritating reflections and view blocking effects of conventional constellations like Starlink cause a permanent nuisance to other users of space like astronomers during flight and deorbit, the constructors of Europe´s constellation IRIS2 are going can count on to receive from HPS an exclusive offer for a special version: the ADEO Stealth Sail –invisible, fully transparent and also available for most satellite types and operational orbits.
As HPS-CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer explains: “Our ADEO deorbit system already presents numerous benefits and applications in satellite end-of-life management like cost- & mass-effective and sustainable deorbiting, compliance with current and future Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines, flexibility and adaptability. Now, with the special stealth version for dedicated to the architects of Europe´s IRIS2 constellation we take the decisive step to let Europe set yet another standard in space sustainability”.

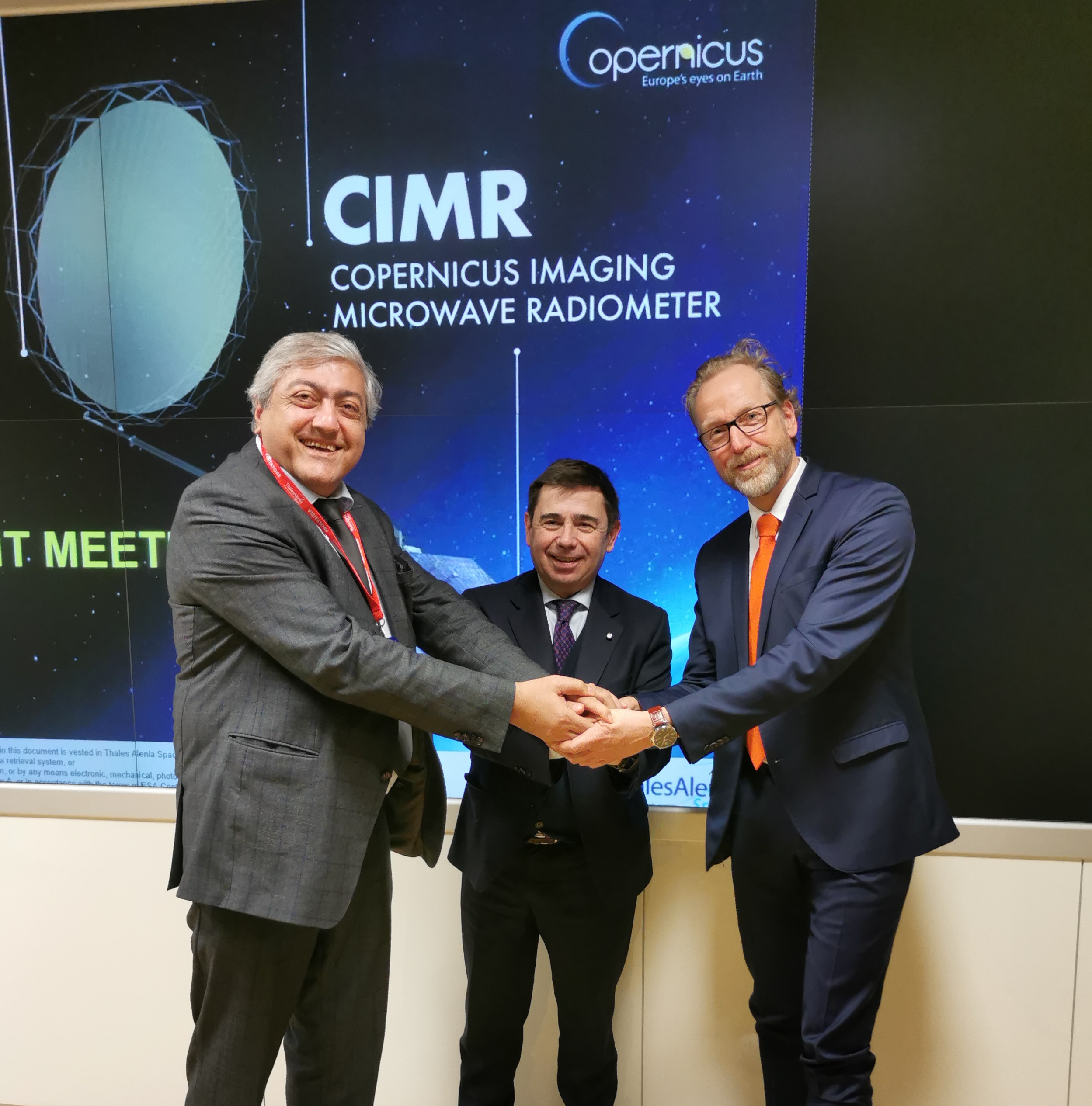
MoU of Space SMEs Aviosonic and HPS to join forces fighting space debris – right in time for Europe´s new constellation Iris2
Mai 2022
Aviosonic´s patented DeCAS for tracking and re-entry footprint prediction extending high-tech-lead of Europe´s satellite deorbit system “ADEO” unassailably
(Munich-Milano, May 10th, 2023). At testified TRL-9 and with solid flight heritage the sail system “ADEO” already is the leading device for quickly deorbiting almost all satellites, thus preventing spacecrafts after their end of mission from becoming as well as producing new space junk for years to come. Because it is a sail, it does not produce any pollution itself, chemical or otherwise, and because this very sail will be in its next version also transparent and absolutely non-reflective, it does not cause any irritations to any space observer on earth. Munich based spacetech innovator HPS, a medium sized company with a subsidiary in Romania and a total headcount of 80, has invested – together with several institutional and industrial partners – 12 years of constant development and qualifying into ADEO, and is now ready to take yet another giant leap by joining innovative forces with Aviosonic Space Tech, Milan/Italy.
Aviosonic Space Tech, born in 2015, owns the patented DeCAS system (Debris Collision Alert System) for in-orbit/de-orbit tracking and re-entry footprint prediction of space vehicles. DeCAS is a 1U mm system which always maintains a constant link with the ground operation center allowing precise information on the satellite position, aliong with the calculation of the re-entry footprint in real time, with the aim of collision avoidance between satellites, satellites and aircrafts as well as to alert government agencies. The technical characteristics and modularity allow DeCAS to be installed on any space vehicle, offering different services depending on the mission requirements. DeCAS, which took part in different space missions, provides a unique service for satellite tracking, decommissioning and re-entry prediction in real-time.
Prof. Piermarco Martegani, CEO of Aviosonic Space Tech says:”The integration between DeCAS and ADEO allows the creation of a unique product on the market capable of strongly implementing the safety of space operations both during orbital and decommissioning re-entry phses, even in the event of failure of the hosting satellite. This safety information is also needed by the Air Traffic Management System. The collaboration between Aviosonic Space Tech and HPS is the demonstration that in order to guarantee safety during space operations, an international cooperation between SMEs is necessary.”
HPS-CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer shows bulletproof confidence in the future of ADEO on the world market and emphasizes: “ADEO has all the facts on its side: first, all space industry badly needs a deorbit device like ADEO, since the faster the sail opens free orbit positions, the longer we can keep space as a sustainable surrounding. And, from second to infinite: ADEO combines TRL9 and flight heritage, offers a comprehensive range of models, beats economically as well as ecologically any other type of deorbit device, also it is already in serial production at HPS. And now we even join forces with the two outstanding innovators in their fields, and others will join, underlining once again what´s at the core of ADEO: 100 percent European, 100 percent SME, 100 percent sustainability in space – and exactly what Europe wants for Iris2.”
Contact for further information:
HPS: Dr. Daniel Stelzl, stelzl@hps-gmbh.com
Aviosonic: Prof. Piermarco Martegani, Piermarco.Martegani@aviosonic.it
ADEO Dossier: German: (https://www.hps-gmbh.com/tag/adeo/)
ADEO Dossier: English: (https://www.hps-gmbh.com/en/tag/adeo-en/)
Video: https://youtu.be/pUeSZzdn_6c
April 2023
All Launch Windows are closing for Satellites Without ADEO or Equivalent Deorbit Tech
After FCC, SpaceX, and ESA now also the three German startups racing for the smaller launchers` pole position in the commercial market made it clear that tickets to space will be available only to satellites prepared to be able to deorbit quickly after service.
The companies made their points recently in statements to the German space magazine “Raumfahrt Concret”.
For more details see: RCI-Newsletter-1-2023.pdf (hps-gmbh.com)
Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS, the German spacetech company that has developed ADEO to become the number 1 deorbit device for spacecrafts on the market, comments: “While we witness many cases of exorbitant differences in opinions when it comes to principles the space industry should follow, it is with great relief that we see this case ruled by unanimous voices echoing the new green spirit of deorbit from everywhere.”

3 – 2 – 1 – Next liftoff for the HPS space sail ADEO-N3 on the satellite carrier ION of the Italian mission provider D-ORBIT
January 2023
3 – 2 – 1 – Next liftoff for the HPS space sail ADEO-N3 on the satellite carrier ION of the Italian mission provider D-ORBIT
Already in the heat of last summer, HPS in Munich was preparing for the third mission of the innovative space brake sail ADEO-N, which unfolds automatically at the end of the mission and drives “its” satellite into the atmosphere to burn up. This technology avoids the formation of new space debris already on the ground and finally makes space missions sustainable.
The ION Satellite Carrier with ADEO-N3 with its sail area of 5sqm has been on board a Falcon 9 since the picture book start on January, 31, 2023 from spaceport Vandenberg, California, now on the way to the target orbit at 270 to 500 km altitude at 53 degrees inclination. Probably by the end of 2023 ADEO-N3 will then, as on previous flights – including one with ION also on Falcon 9 – deploy the braking parachute and remove its ION Satellite Carrier from orbit without leaving any residue many times faster than usual. With the flight heritage accumulated by then, the mature ADEO system heralds a “green” space age. Because at least for European missions or missions from Europe, there will – in all probability – no longer be any more launches without deorbit tech on board: The Green Deal of the EU will then also apply to “clean-green missions” in space.
On the current flight, ADEO-N3 acts as another verification of maturity for HPS. D-Orbit and HPS already captured what will happen high above the earth during a nominal mission as historical testimony on video during the last flight:
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7021106640993021952
Video is free for publication
The attached video, recorded directly on site with the on-board camera of the ION satellite of the Italian cooperation partner D-Orbit, provides live proof: with the product of HPS, which is now ready for series production after twelve years of development with great support from ESA, DLR and the Bavarian government, a new era of responsibility in space is beginning. ADEO is manufactured in series by HPS at its sites in Munich and Bucharest, primarily for constellation satellites. ADEO products are available for satellites weighing up to 2,500 kilograms at flight altitudes of up to 800 km. Even higher-flying satellites can be operated with ADEO if they have previously lowered their orbit accordingly using their own propulsion. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “With ADEO on board, satellites do not become space junk in the first place. And at conditions that are ALWAYS more economical than all other options.”
Largest joint innovation project in European spaceflight: CEOs of TAS-I, HPS and LSS kick off
January 2023
Largest joint innovation project in European spaceflight: CEOs of TAS-I, HPS and LSS kick off Phase C/D of the large deployable antenna “LDRS” in the CIMR project
Since the spectacular win of the €110 million contract in 2020 for the development and construction of an LDRS (Large Deployable ReflectorSubsystem) by the SME consortium led by HPS, the project supporting to secure a sovereign European level of innovation has been running like on rails despite all its complexity. The confidence of the end customer ESA and its prime contractor TAS-I for the mission, which has grown steadily over the course of the project’s development, has now found expression on 23.01.2023 in the sealing of the departure into Phase CD by the signing of the so-called “RIDER” for the construction and testing of a qualification model (EQM) in 2023/2024, followed by no less than two flight models (PFM and FM2).
The supporting technology pillars of the innovation project are, in addition to the main innovation partners LSS (development, construction and test of the large deployable reflector), the HPS subsidiary HPtex (mesh production for the reflector), FHP (CFRP struts for the reflector), INVENT (CFRP tube for the deployable arm) and vH&S (for the deployment control electronics), further 10 companies from seven European countries under the consortium leadership of HPS.
The Environmental Observation Mission under the Copernicus Earth Observation Program of the European Union is an essential element of the European Space Strategy as a highly ambitious project in the field of climate observation and the understanding of effects of climate change.
Photo (TAS-I): contract sealing – center: Massimo Camparini (CEO of the space company ThalesAleniaSpace Italy) and the CEOs of HPS, Ernst K. Pfeiffer (right) and of LSS, Leri Datashvili.

January 2023
Historical video evidence
from HPS and D-Orbit
On December 15, 2022, at 12:10 UTC, the world’s unique ADEO braking sail from the German space technology company HPS GmbH, Munich, opened the chapter of sustainability for international spaceflight 500 kilometers above the Earth: as planned, on time and precisely, the sail attached to the ION SCV 003 satellite unfurled over an area of 3.6 square meters to remove “its” satellite from orbit in the shortest possible time without leaving any residue, thus avoiding hazards for other space vehicles and making room for the next generation of satellites at its former orbital position. Preliminary studies and calculations indicate that this will reduce the descent time not by half, as originally expected, but rather by as much as five times.
The attached video, recorded directly on site with the on-board camera of the ION satellite of the Italian cooperation partner D-Orbit, provides live proof: with the product of HPS, which is now ready for series production after twelve years of development with great support from ESA, DLR and the Bavarian government, a new era of responsibility in space is beginning. ADEO is manufactured in series by HPS at its sites in Munich and Bucharest, primarily for constellation satellites. ADEO products are available for satellites weighing up to 2,500 kilograms at flight altitudes of up to 800 km. Even higher-flying satellites can be operated with ADEO if they have previously lowered their orbit accordingly using their own propulsion. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “With ADEO on board, satellites do not become space junk in the first place. And at conditions that are ALWAYS more economical than all other options.”