Innovative Space Technology for Sustainable Satellite Disposal and Mitigation of Space Debris in the Spotlight
Unusual Event at SpaceTech Expo Bremen: HPS Hardware Handover at the OHB Stand
November 2025

Innovative Space Technology for Sustainable Satellite Disposal and Mitigation of Space Debris in the Spotlight
Unusual Event at SpaceTech Expo Bremen: HPS Hardware Handover at the OHB Stand
November 2025
Unusual Event at SpaceTech Expo Bremen: HPS Hardware Handover at the OHB Stand
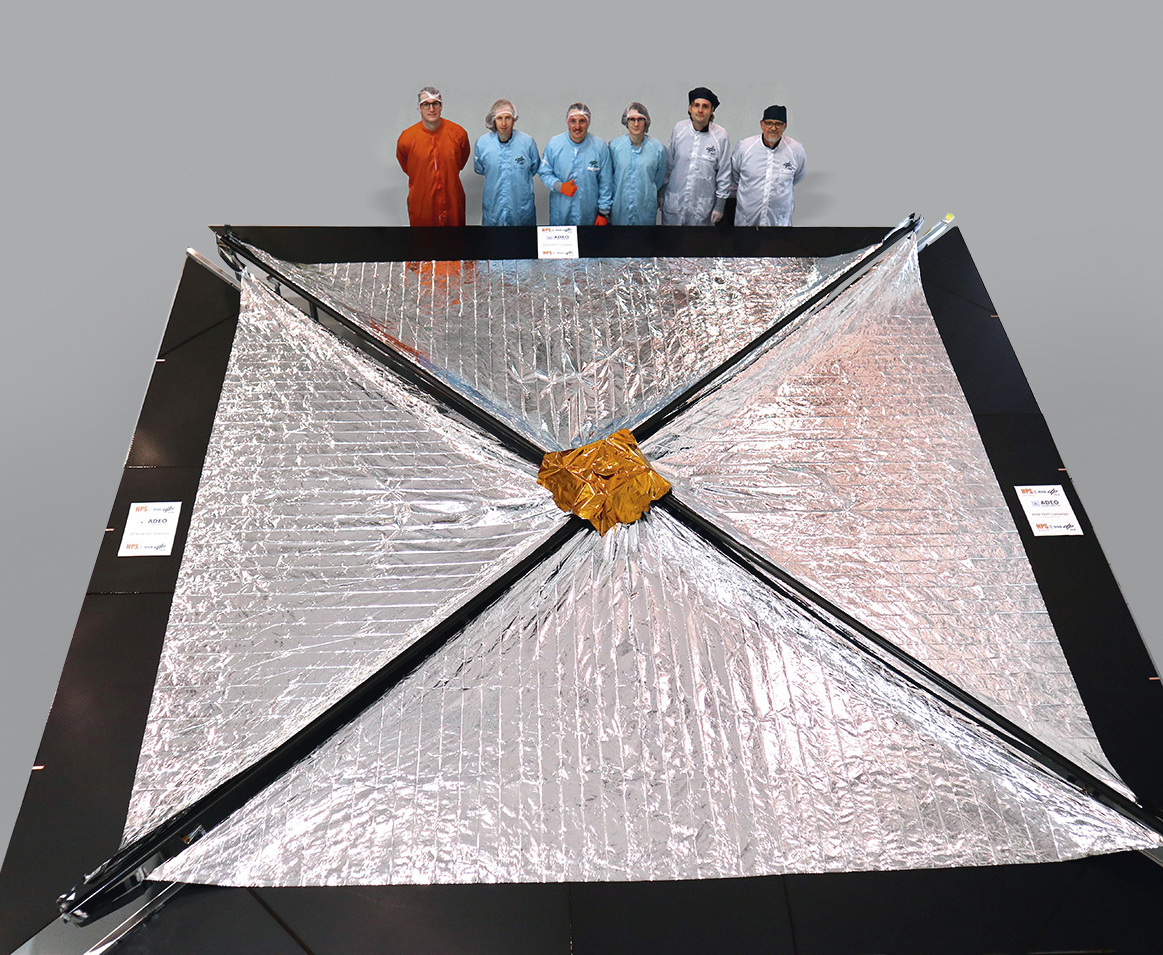
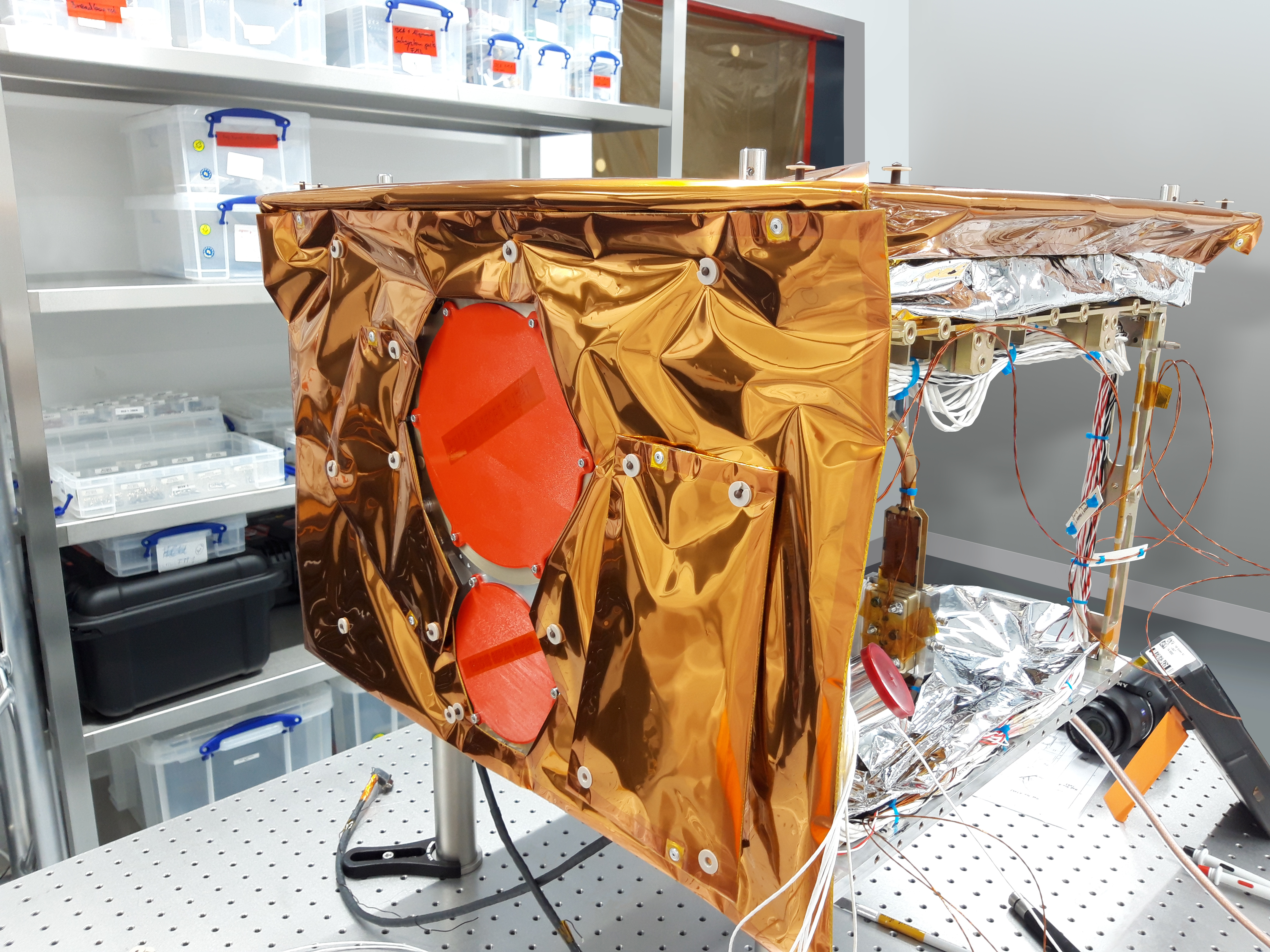
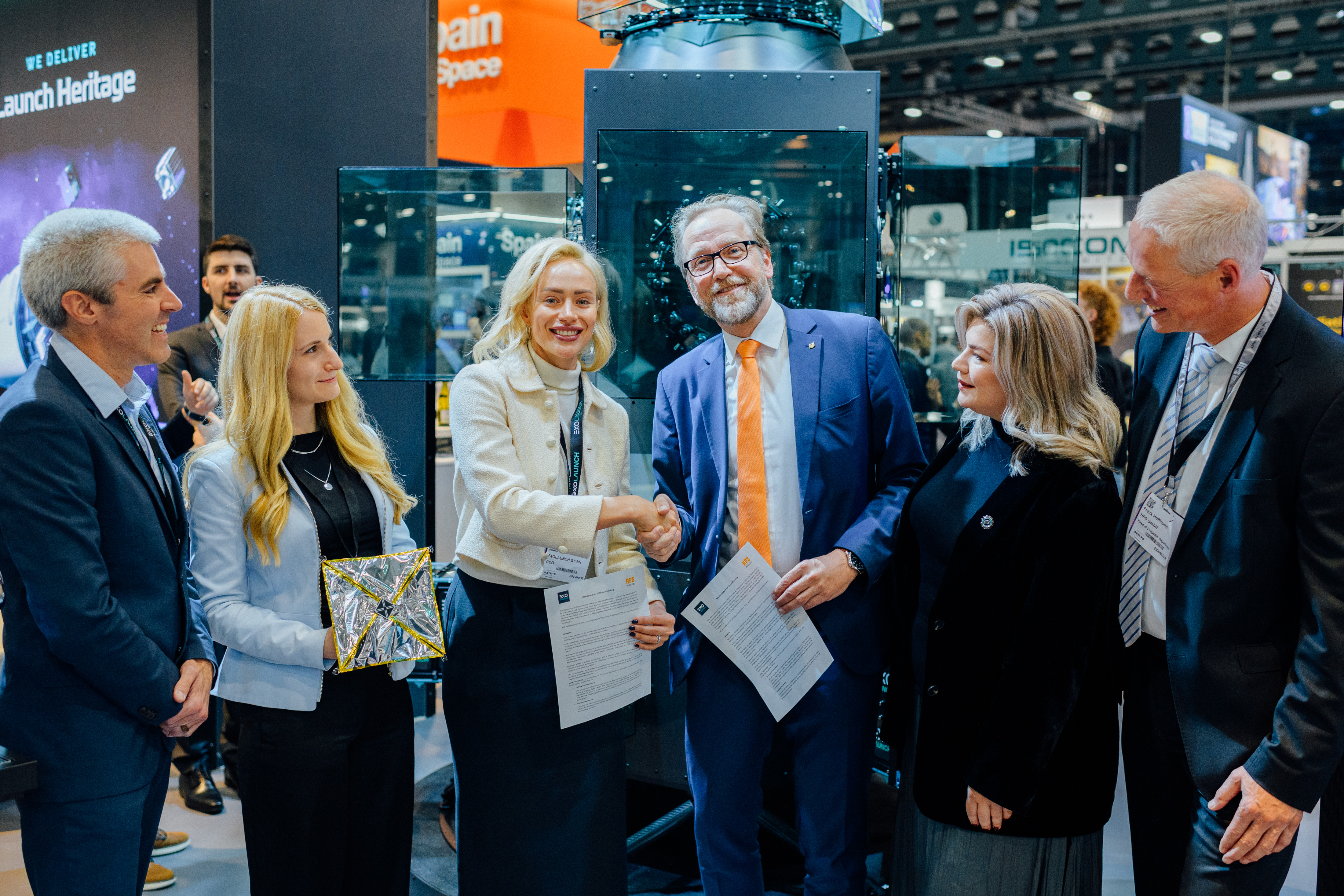
On 19.11.2025 at 15:30, an extraordinary event for a trade fair of this kind took place at the SpaceTech Expo stand of the German space company OHB in Bremen: For the first time, genuine ADEO hardware was ceremoniously and personally handed over between HPS (CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer and CFO Peter Rauhut) and OHB (CEO Chiara Pedersoli and Member of Management Board Gianaldo Mantovani) for integration into a new satellite constellation – marking a strong, tangible sign of innovation and sustainability in the space sector.
HPS GmbH Supplies Drag Sails for Safe Satellite Deorbiting
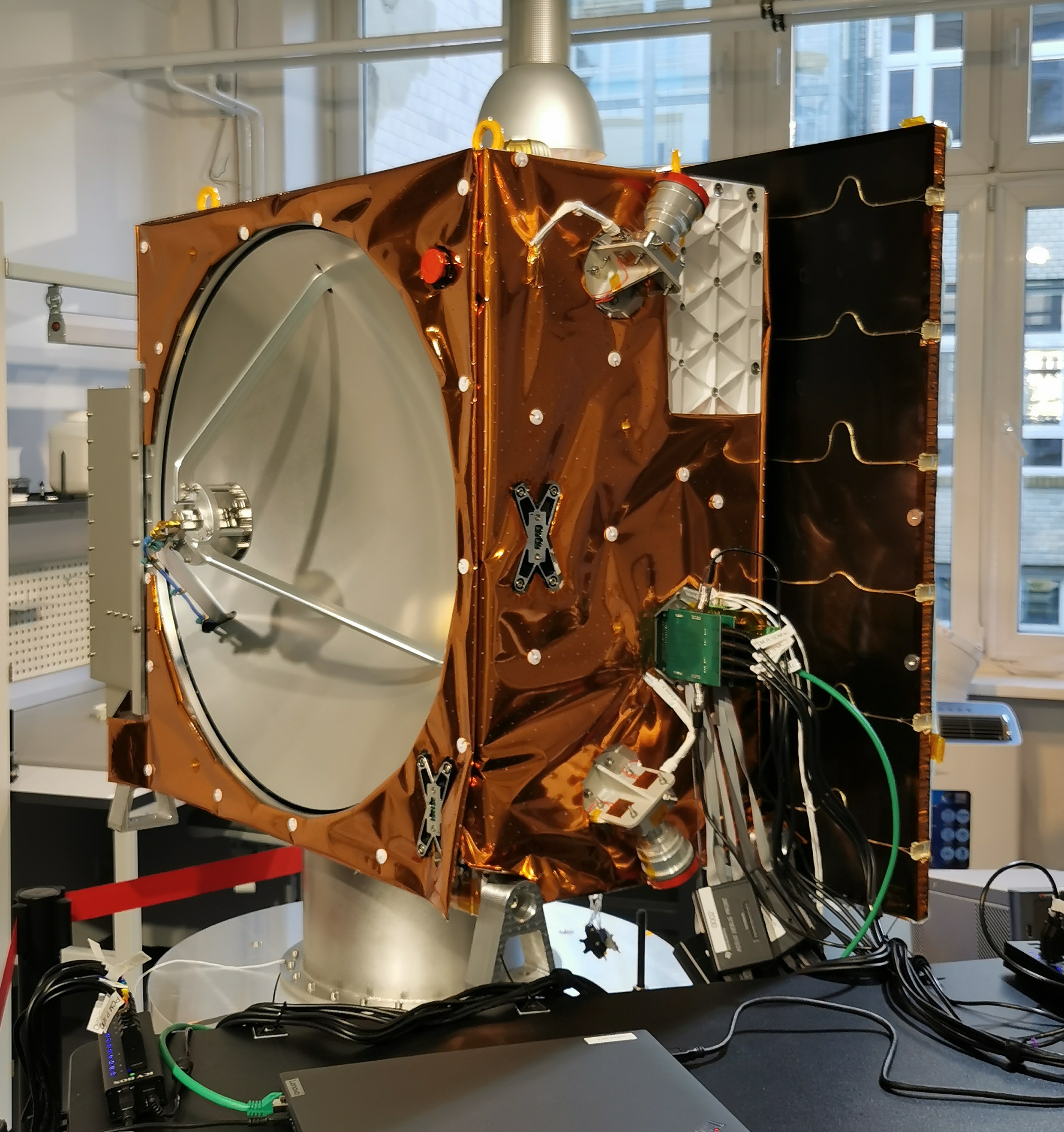
The Munich-based high-tech company HPS GmbH (headquartered in Munich, with a subsidiary in Bucharest) delivered four ordered ADEO-N(ano) class drag sails to its client, the renowned space company OHB, in Bremen. The ADEO modules are essential for the accelerated deorbiting of satellites at the end of their service life, ensuring compliance with the legal requirement of a maximum five-year deorbit period.
Technological Responsibility and Collaboration for Sustainable Space Activities
HPS is the developer and manufacturer of the ADEO product family of drag sails, designed for satellites of all sizes and weight classes in LEO and MEO orbits. Both companies – HPS and OHB – are also among the first signatories of the ESA Zero Debris Charter and are jointly as well as individually committed to its consistent implementation. By integrating ADEO into its LEO-PNT satellites, OHB underscores its top-level support for sustainable space activities, as well as for close collaboration between large system integrators and SMEs, which is of great and ever-increasing importance, especially in the context of European defence initiatives.
Significance of the Partnership and the Project
For HPS, collaboration with OHB is of particular relevance. For example, HPS supplied the downlink antenna for the OHB satellite of the HERA mission. The current delivery concerns a space programme of immense reach: the LEO-PNT satellite constellation is part of the ESA programme for the next generation of highly precise navigation and positioning technology in space. In general, ESA is committed with great dedication to consistently implementing its five-year deorbit requirements in its missions.
SpaceTech Expo Bremen as a Stage for Innovation and Sustainability
With its numerous space technology models and information stands from around one thousand exhibitors, the SpaceTech Expo in Bremen provided a unique backdrop for the handover of the ADEO modules, which are scheduled to launch into space in 2026. The timing of the fair and the already planned handover coincided by chance, so both companies spontaneously decided to celebrate this event as an extraordinary moment.
Dr. Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS GmbH, emphasised: “There is no better way to draw attention to pioneering technologies for the avoidance of space debris with a strong presence at by far the most important space fair in Europe – where all relevant institutions and companies of the industry are gathered. The ADEO modules of the N-version delivered here, are among the most in-demand ADEO-class of drag sails currently available.”


Current Status of the Satellite Project in Kruibeke, Belgium
November 2025
Back in July this year, it was announced that Redwire Belgium has also adopted HPS’s ADEO drag sail technology for satellite deorbiting. HPS is a global pioneer in developing sustainable space resource utilisation, and with its ADEO drag sail product family for all satellite classes in LEO orbits, it has established the international gold standard in deorbiting technology.
For Redwire’s current satellite project, HPS delivered the ADEO-L version – constructed under the ESA-GSTP-project umbrella of ADEO2 – of the drag sail in the summer. The Redwire spacecraft, developed specifically for an IOD/IOV mission in LEO for the European Commission, has medium-sized dimensions and therefore requires the ADEO-L deorbit module, featuring a surface area of 25 m².
The ADEO2 deorbit module was successfully integrated onto the satellite at the Redwire Satellite Processing Facility in Kruibeke, Belgium, on 3rd and 4th November 2025.
The next step will be comprehensive system tests of the fully integrated satellite—including environmental tests such as vibration, acoustic, and thermal vacuum (TVAC) testing—scheduled for the first quarter of 2026. The launch is planned to take place later in 2026 aboard a European launch vehicle, which is yet to be selected. Deployment of the drag sail for rapid and efficient deorbiting at the end of the mission is planned for about 1.5 years after launch.
As an integrated aerospace and defence company, Redwire focuses on autonomous systems and cross-domain operations utilising digital technology and AI automation. Redwire’s approximately 1,300 employees in the United States and Europe are developing innovative space and airborne platforms that are shaping the future of multidomain operations. The Belgian facility of Redwire can look back on more than 40 years of experience in spaceflight, during which it has developed spacecraft platforms and delivered innovative technologies for groundbreaking ESA programmes.

New in-orbit demonstration CubeSat project with Deployable Membranes based on ADEO-M
October 2025
The OPTIMIST mission, kicked-off in August 2025 to undergo a Phase A/B1, will involve a CubeSat deployed at an altitude of about 550 kilometers for one year. Its main goal will be to mature and validate the SAILOR payload technologies via statistically measuring near-Earth submillimeter, millimeter and centimeter sized debris populations and using a large deployable membrane (5–7 m²) equipped with acoustic sensors and a camera system. These instruments will detect and analyze impacts from small debris, providing valuable data for future, larger-scale missions: OPTIMIST will field-test essential technologies for the final target, the full-scale-mission SAILOR, which is dedicated to the scientific objective to investigate in-situ small space debris and its evolution. The results of the precursor mission OPTIMIST, to be launched in late 2027, will support the feasibility and design of a robust debris detection platform, which can be used with several satellites in the layer of a large satellite constellation for better debris impact predictions.
The first milestone of the project has already been completed with successfully closing the Mission Baseline Review with ESA. The Phase A/B1 study with breadboarding activities assesses technologies identified in SAILOR’s earlier phase, define mission architecture and evaluate launch options—favoring European launchers. Trade-off analyses ensure the mission is designed for maximum reliability and cost-efficiency, while meeting all technical requirements.
Under the project-lead of C3S (Hungary), HPS-Germany is responsible for the deployable membrane module, which is based for the OPTIMIST Mission on HPS’s deorbit module ADEO-M. HPS-Romania will perform the membrane manufacturing and the acoustic sensor bonding process. Further project partner under the prime C3S is University of Kent (UK) ensures extensive knowledge at the space debris science part and access to facilities to perform experimental simulation of hypervelocity impacts.
With SAILOR’s closure of Phase A and start of Phase B1 and the incorporated by the OPTIMIST precursor study, the SAILOR-project is poised to make significant progress toward safer and more effective management of space debris, paving the way for future missions that will help protect Earth’s orbital environment. SAILOR and OPTIMIST are part of ESA’s Space Safety Programme (S2P), which is dedicated to protect Earth’s and in-orbit infrastructure from dangers from and in space.

Redwire Belgium also relies on the gold standard of deorbit technology: the ADEO dragsail from HPS
July 2025
Twelve years ago, it was just an idea: quickly and inexpensively removing spent satellites from space traffic – quite simply with an automatic brake sail. Today, HPS, the global pioneer of development to ensure the sustainable use of space as a resource, is the international gold standard in deorbit technology with its ADEO dragsail product family for all classes of satellites on LEO orbits. From experimental university projects to global constellations: satellite manufacturers and operators from the EU and Asia, Australia and America rely on ADEO to reliably dispose of their spacecraft within the prescribed window of a maximum of five years after the end of operation.
The latest example: US-corporation Redwire´s branch in Belgium. The integrated aerospace and defense company focusses on autonomous systems and multi-domain operations leveraging digital engineering and AI automation. Redwire’s approximately 1,300 employees located throughout the United States and Europe are committed to delivering innovative space and airborne platforms transforming the future of multi-domain operations.
Redwire’s facility in Belgium has more than 40 years of spaceflight heritage developing spacecraft platforms and success delivering innovative technology for game-changing ESA programs.
The spacecraft specifically designed for this mission will operate on LEO. Its weight as a midsize satellite requires a deorbit module of the ADEO-2 class series, which is now with integrator Redwire. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “We at HPS in Munich and Bucharest are delighted to be able to count this prestigious customer Redwire among our ADEO customers. The importance of Redwire´s role model function for others as a responsible space company cannot be overestimated.”

ADEO shines at the “International Symposium on Space Sailing” 2025!
July 2025
This week, at the “7th ISSS” in Delft (NL), HPS is proud to represent Europe’s leading deorbit solution: ADEO – the dragsail for a sustainable orbit.
With the presentation by our project manager Dorottya Milankovich on Day 1, June 30th, we’re showcasing:
HPS CEO on site: “We are proud to be part of this very specialised space sailing family, ranging from solar sail developers to dragsail suppliers, from radiation scientists to sailing simulation experts.”
In total 82 participants from all over the world listened on site and via online, from USA to Philippines, from NASA to TU Delft.
This Symposium proved:
ADEO is not just a product – HPS is one of the world market leaders for deorbit dragsail modules.
Let’s sail toward a cleaner orbit!
#ADEO #Dragsail #ZeroDebris #CleanSpace #SpaceDebris #ISSS2025 #SpaceSustainability #HPS #SpaceTech #Delft #TUDelft #LEO #SpaceSailing #ESA #SatelliteDeorbiting #Deployables #SolarSailing


HPS prominently present at ESA’s Zero Debris Week
June 2025
From 10 to 12 June 2025, everything at ESA’s European Space Operations Center in Darmstadt will be dominated by the highly ambitious “Zero Debris Program” of Europe’s space agency. The days are divided into two large action chapters: from June 10-11 at noon, the Zero Debris Future Symposium will focus in particular on high-level discussions of non-technical aspects, such as the future direction of the Zero Debris Initiative and its community, as well as commercial and political challenges in connection with orbital debris. Day two, June 11-12 at noon, will be dedicated to another working session on the Zero Debris Technical Booklet. Among other things, the technical leaders who will oversee the next edition of the booklet will be elected on this occasion. The participating organizations will also discuss how they have used the booklet so far, how the work on the booklet should be regulated and organized, and how the technologies listed in the booklet can be implemented.
The Zero Debris Technical Booklet published on January 15, 2025 lists technologies that ESA believes will contribute to achieving the goal of zero debris by 2030. The booklet is essentially a technical zero debris “to-do list”. The aim is to minimize the release of new debris and reduce its impact on people, infrastructure and the Earth’s environment.
Developed by a team of engineers, operators, lawyers, scientists and policy experts from a wide range of institutions in the Zero Debris community, the booklet identifies six key technology objectives that are essential to achieving Zero Debris goals:

ESA itself is focusing its efforts on the development of debris-resistant materials and technologies, the design of satellites that can be easily removed from orbit and do not burn up on re-entry into the atmosphere, and finally the development of standardized interfaces for efficient removal in the event of a malfunction.
Beyond the satellite itself, the focus is also on new systems to remove all components of the launch vehicle from orbit. Another source of debris are small particles released by certain types of fuel and pyrotechnics in orbit during deployment. Alternatives are to be developed for this. The distribution of space debris around the Earth highlights the importance of collision avoidance measures. Once the satellites are in operation, much can be gained by optimizing collision avoidance processes and space traffic management. A key element is improving tracking capabilities for smaller, currently untrackable debris objects to refine risk assessment.
Operational practices can also be optimized, supported by new technologies to improve communication infrastructure and spacecraft health monitoring. At the end of a mission, the deorbit and re-entry process (for LEO and MEO satellites) and the impact on the environment need to be considered. Active debris removal services are required in orbit, as well as reducing the environmental impact of debris re-entry on the ocean and atmosphere, which will begin with further research.
Participation in ESA’s Zero Debris Initiative is a top priority for HPS – and accordingly, HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer will take part in the central program items on both days in Darmstadt. HPS’s commitment goes far beyond academic aspects, as the company has already made a remarkable contribution to avoiding space debris with its ADEO Deorbit Module product family by rapidly removing disused satellites from orbit; in addition, it is already on the threshold of Phase B with initial developments for a detector for previously undetectable particles from 0.1 to 10 mm in size called SAILOR.
The HPS boss doesn’t mince his words when it comes to emphasizing the importance of the ESA initiative: “The Zero-Debris Initiative is a start, but we are still a long way to our goal. We still have to reach an important milestone, and that is directly in the minds of the target groups: In parts of the space community, the debris issue is still seen as merely a green nice-to-have topic. This is absolutely wrong: it is an issue of great commercial interest and value, because if the littering of orbits continues at this rate, economically viable activities in space will soon be history – and that so before they have really taken off.”
HPS puts ADEO know-how at the service of ESA´s Hungarian Prime C3S
May 2025
It seems to be a basic law of nature: Wherever and however humans are active, they end up producing large quantities of waste. To suppress the problem, many terrestrial areas, the oceans and, in recent decades, outer space itself have become dumping grounds. However, the latter in particular is now threatening to take radical revenge, as flying debris from previous space missions is increasingly becoming a threat to all other activities, especially in the most frequented orbits between 200 and 1200 kilometers.
While large debris such as burnt-out rocket stages are the easiest to detect and can be avoided by new guests in orbit, it is the small projectiles, flying with 5-10 km/s orbital speed, which have often shrunk below millimeter size as a result of previous fragmentations, that pose the greatest threats. Even one millimeter-sized debris impact can render a satellite inoperable. Emerging their threat further, their flux increases significantly as their size decreases, with the consequence that the much more frequent impacts of debris of this size can pose a far greater risk to space operations than the more dramatic catastrophic incidents.
However, only larger debris can be observed and tracked from the ground – but not in the critical range of 0.1 to 50 mm. Therefore, measurements in situ, i.e. directly in orbit, are urgently needed to make it possible to describe the Earth’s flying garbage dump with sufficient reliability in the first place. After critically weighing up the alternatives, ESA has turned its attention to a possible large-area detector based on the successful ADEO deorbit sails from HPS. If the sail membranes are now equipped with acoustic sensors and cameras on board, it will be possible to measure the dust flow in the required size range. The name of the project: SAILOR – Sail Array for Impact Logging in Orbit.
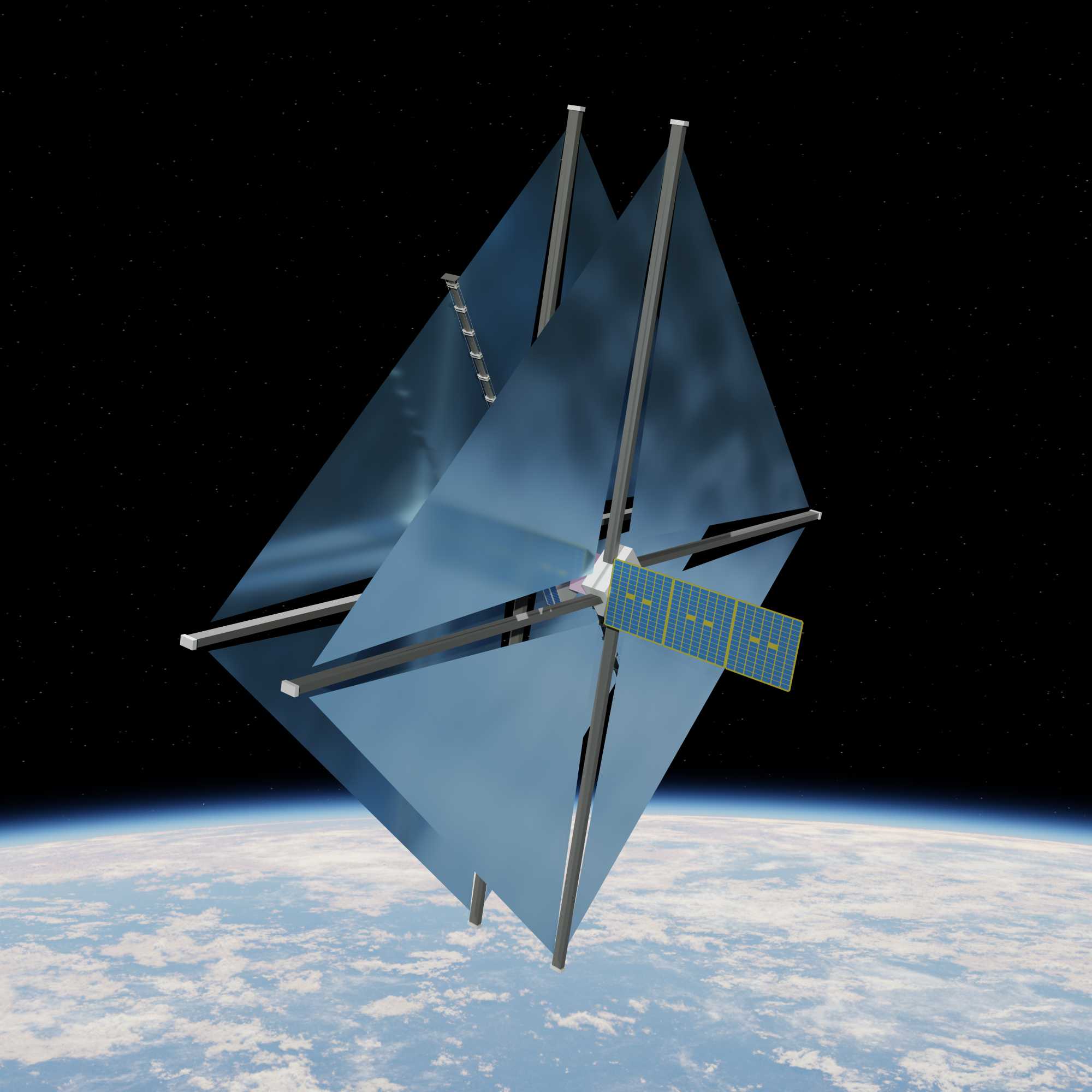
The spacecraft consists of two large detector surfaces 100 cm apart. The two sails have an exposed surface area of 25 m2; in the ADEO program, they are the main actors of the large dragsail versions under the name ADEO-L. The membranes are around 10 μm thick and are held in position by extendable cross booms. The booms are stowed together with the sail membranes during launch and deployed in orbit. The deployment module in which booms and sails are integrated, consists of a deploying mechanism with a motor that pushes the boom arms outwards. A system of multiple cameras is mounted to a separate boom to document the holes created on the inner surface of both sail membranes. Acoustic sensors are attached to the sails to detect an impact in real time. The interaction of SAILOR’s technical equipment will ultimately allow the density, speed and trajectory of the small debris to be determined.
The ambitious ESA project SAILOR is currently in the transition from Phase A to Phase B1, which will also include the construction of breadboard models of the spacecraft and its electronics as well as the associated test programs. It also involves these steps:
Overall, the specifications of the project in this phase should lead to a positive decision at the ESA Ministerial Council meeting in Bremen in November 2025 on the continuation of a three-year mission at an altitude of 850 km to be launched in 2031/2032. The industrial team proposes a small precursor CubeSat mission, called OPTIMIST after this type of sailboat, to test the sensor technology using an approx. 10 m2 membrane as early as 2027/2028 as risk mitigation for the full-scale mission.
The industrial structure behind SAILOR also stands for this. This is because C3S, a leading Hungarian aerospace company, is acting as prime contractor for an ESA project of this kind for the first time, drawing on the expertise of ADEO inventor HPS GmbH as a subcontractor for the deployable membrane subsystem. C3S is also planning work shares for HPS in Romania. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “The great enthusiasm with which we have taken on our role in this project rests on three pillars: firstly, it is existentially important for the space industry as a whole; secondly, it is an opportunity for us as HPS to impressively demonstrate the versatility of the ADEO technology from our company; and thirdly, we consider it eminently important in Europe that the industrial talents of Hungary and Romania are finally brought to light in an appropriate way, and that in a joint mission. We at HPS are delighted to be working under the project management of C3S.”
Cubesat-UDAN: CDR successfully completed – a major milestone for Europe’s disruptive antenna technology
April 2025
NewSpace relies primarily on small satellites. However, their efficiency is primarily based on antenna performance: the smaller the satellite, the lower the antenna performance and the more expensive it is to technically compensate for this on the ground. The solution from HPS Munich and its Romanian subsidiary in Bucharest: an antenna that can be deployed outside the satellite in the form of a 50 cm high conical quadruple helix and 90 cm diameter ground plane with the additional advantage that it can be scaled to even lower or higher frequencies than the planned bandwidth of between 410 and 460 Mhz but always keeping a gain above 10 dBi. Stowed together for the launch phase, the antenna package is only 10x10x15 cm in size.
ESA was convinced and awarded the development contract in 2018 within its ARTES program to the German specialist for deployable antennas, HPS GmbH in Munich and its Romanian subsidiary HPS S.R.L., Bucharest. In the meantime, the German Space Agency at DLR has provided further ARTES funding to maximize efficient development.
We are delighted that the next major milestone has also been passed with flying colors: the punctual completion of the CDR phase in March 2025. This will now be followed by the production of the engineering model in the second and third quarters and then the test campaign; the contract ends in the fourth quarter of 2025. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer comments “With this project completion, HPS will raise UDAN’s maturity level to TRL 6 and then finally to TRL 9 with a planned in-orbit demonstration (IOD). This means nothing less than clear the way for the latest generation of antenna technology on the commercial NewSpace market!”
HPS with ADEO product family: top position in NASA’s technology report extended
March 2025
A year ago, the deorbit module from HPS took its place at the top of the podium of the most important technology achievements according to NASA. This was because ADEO already had everything that the American space agency considered crucial for success at the time: top values up to TRL9, scalability and proven flight heritage. Exactly one year later: ADEO, now supplemented in the technology report by the presentation of the bestsellers ADEO-Cube and ADEO-Pico, maintains its position both against numerous Dragsail competitors and against other passive deorbit technologies.
HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer comments: “With ADEO, we are surfing at the top of the wave worldwide that we have created ourselves with this technology over many years of R&D – often with significant co-financing by ESA and DLR plus considerable company resources. And we are actually delighted with every attempt by other companies to establish deorbit sails on the market: The bigger they make the wave, the higher our product family sails on its crest.”

ADEO – Space Heritage
January 2025
ADEO (Atmospheric Deorbit Sail Module) is the name for an entire product family of drag sails for satellites from the German space company HPS, Munich. They accelerate the disposal of satellites from space to a period of less than five years and thus fulfill the prerequisite for the satellite to receive approval for launch into space in the first place.
The sail is scalable and available in many variants from series production. ADEO-N is tailored to small satellite missions of 20-250 kg, while the ADEO-M and ADEO-L series are designed for larger missions of 100-700 kg and 500-1500 kg respectively. The ADEO-N series corresponds to a sail size of 5±2 m2, while ADEO-M covers areas of 15 ± 5 m2 and ADEO-L 25 m2 and more. However, smaller versions have also been available for a year, especially for cubesats, e.g. an ADEO-P for 1U-6U satellites (1-20 kg) and an ADEO-C for larger cubesats (5-50 kg). A total of five versions are currently available to order, all of which reliably dispose of satellites from LEO – including those from higher MEO orbits when combined with satellite’s onboard propulsion – within the required time frame. A corresponding configurator for selecting the perfectly suitable ADEO module is available for individual mission calculation (ADEO Online Configurator).
Now there is a short film about the production and testing of the product family, as well as ADEO’s heritage story:
Based on over ten years of development, HPS has successfully completed a series of missions up to “full burn” and has thus firmly established itself at the top of deorbit technologies at qualification level TRL 9.
2018: ADEO-N1 (“NABEO”) was launched on a Rocket Lab Electron rocket kick stage back in 2018, with Peter Beck himself (CEO RocketLab) even personally handling the sail. On this flight, the sail was unfurled just 90 minutes after the launch. Visual ground observations confirmed the successfully deployed sail and its performance.
2021: In June 2021, ADEO-N2 (“Show me your Wings”) was launched into space by the spacecraft carrier ION-003 of the Italian launch service provider D-Orbit, as part of SpaceX’s Transporter-2 mission. The successful deployment of the sail in December 2022 was recorded by the ION carrier’s on-board camera. The integrity of the sail after one year in orbit was confirmed, again by means of the onboard camera. On December 8, 2024, HPS received confirmation that ADEO-N2 had completed its mission with deployment of the dragsail at 506 km orbit altitude in a record time of just two years after the 210 kg satellite’s “end-of-business” with fireworks of success at 120 km orbit altitude, beating international rules and regulations by three full years.
Even NASA ranks the ADEO module from HPS as the number one automatic passive deorbit technology in view of the qualification and Flight Heritage.
ADEO is now a bestseller not only with European institutions and companies, but also in the fully commercial markets of the USA and Canada.
Highest qualification levels, proven reliability and flight heritage combined with scalability, availability and attractive pricing make the ADEO product family a highly visible beacon in the global field of deorbit systems for all satellites that must comply with the new 5-year deorbit requirement to obtain launch authorization.
Click here for the latest clip about ADEO
————————-
Video: © HPS GmbH, Munich, Germany, www.hps-gmbh.com
Production: Daniela Creutz, www.bluecirceproductions.com
————————-
Two HPS contributions on board the Transporter 12 mission on January 14, 2025
January 2025
Even HPS has never done this before: two of the company’s products are on their way to a sun-synchronous orbit on a Falcon 9 mission. This has been made possible by the rideshare- version of the SpaceX rocket named “Transporter 12”.
On the one hand, the contributions from HPS relate to the highly innovative BANT-1 reflector antenna for Reflex Aerospace’s premiere satellite – see also the HPS news item “HPS congratulates Reflex Aerospace” from today, January 14.
On the other hand, a contribution from HPS itself is the premiere. For the first time, HPS Germany and HPS Romania have jointly prepared a flight hardware with the MLI insulation of the central radiator in such a way that the thermo-optical properties of the satellite are maintained even under the most adverse conditions in space.
The satellite is Sky Bee-1 and part of a thermal infrared constellation HiVE that provides highly accurate yet cost-effective daily temperature data of the world’s land surfaces with a resolution of 30 meters for the benefit of agriculture, urban and industrial environments. The HPS teams of both European countries warmly congratulate their client OHB on the launch success. The first flight model SkyBee-1 is being developed under the InCubed Programme, co-funded by the European Space Agency.

Space premiere also for the innovative BANT-1 reflector antenna from HPS
January 2025
On January 14, 2025, “SIGI”, the first satellite from the NextSpace company Reflex Aerospace, Berlin/Munich, was launched on board a Falcon 9 – Rideshare Mission Transporter-12. “NextSpace” is the term legally reserved for exclusive use by Reflex to describe the new speed in the development, production and provision of space technology, coupled with innovative versatility as a leitmotif for the performance of the product.
To a large extent, this also applied to an essential element of the satellite not manufactured by Reflex: the core broadband reflector antenna developed by HPS from the medium-sized space technology company HPS GmbH (Munich, Germany) with a cavity-backed spiral antenna as an axial feed for a wide bandwidth and considerable gain – and all that from order to delivery in just 12 months.
HPS congratulates Reflex Aerospace on the first launch of one of its products and looks forward to working with them on further NextSpace challenges in space.

Pictures by SpaceX
Dezember 2024
UDAN – The new generation of communication antennas for small satellites
Disruptive development by HPS for the new space sector
HPS, the Munich-based specialist for innovative antenna technology, has entered the realization phase of a fully functional engineering model (EM) with its in-house development “UDAN”. With the HPS design of a deployable conical quadruple helix, UDAN meets the requirements for the smallest possible space requirement during satellite launch as well as an antenna performance that was previously not possible on small satellites.
See deployment video from UDAN breadboard.
The pack size is only 10x10x15 cm (1.5 U), yet UDAN achieves 10 dBi minimum on usable bandwidth between 400 Mhz and 460 Mhz. When deployed, UDAN measures 50 centimeters in height with a diameter of 90 centimeters. Further scaling across the frequency ranges from 100 to 1000 Mhz is planned in order to diversify the service requirements of the communication satellites.
The development is being funded by ESA as part of the ARTES programme, while the German Space Agency at DLR is providing additional funds to maximize development efficiency.
This brings the completion of the CDR phase for February 2025, the production of the engineering model in Q2-3, followed by the test campaign and the closure of contract by Q4 in 2025. With the final completion of the project, UDAN will reach maturity level TRL 6, the in-orbit demonstration (IOD) which is planned to follow in Q2 2026 will then finally raise the HPS innovation to TRL 9 and thus reach out for the commercial market.

November 2024
HPS and EXOLAUNCH: Making Space Clean Again
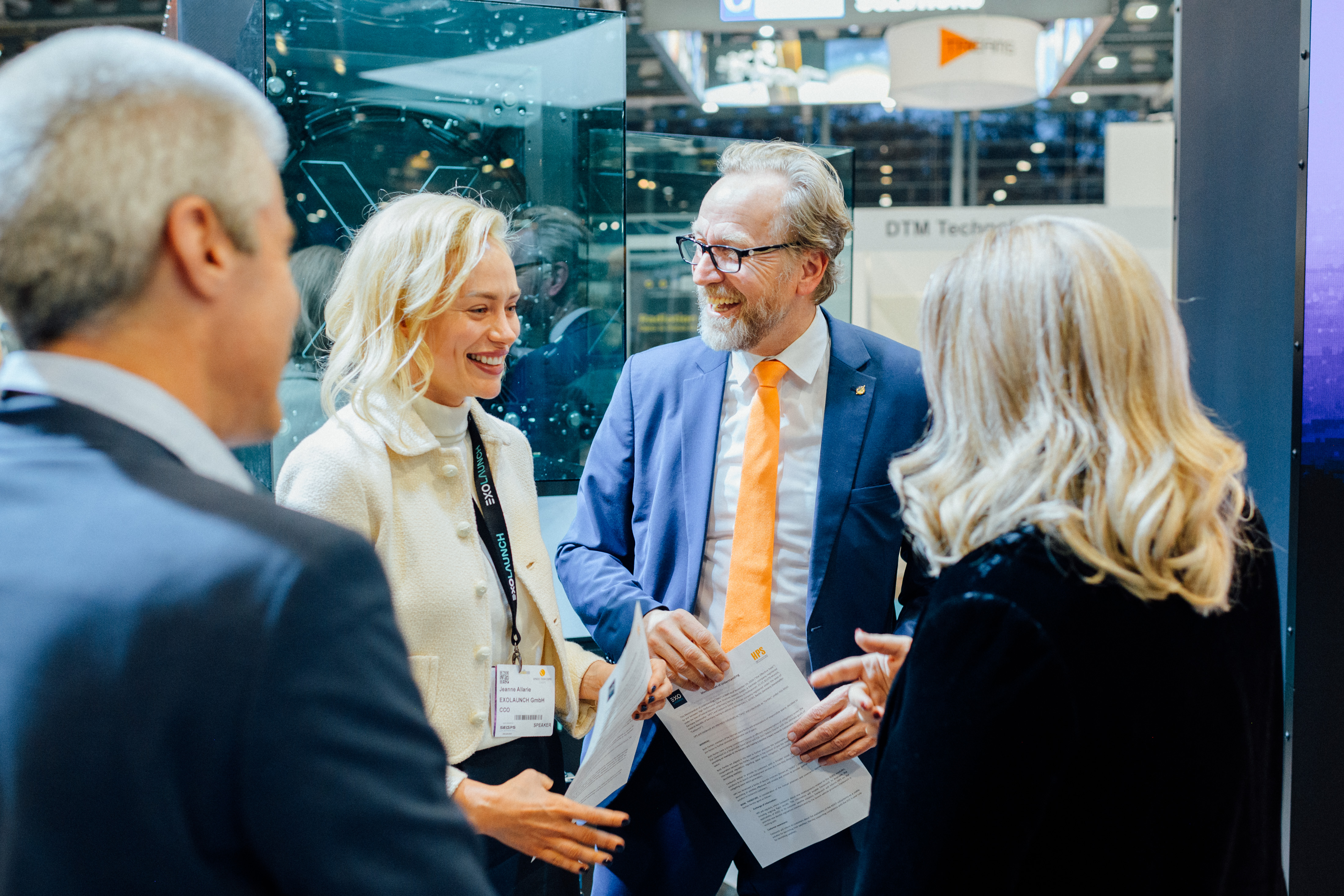
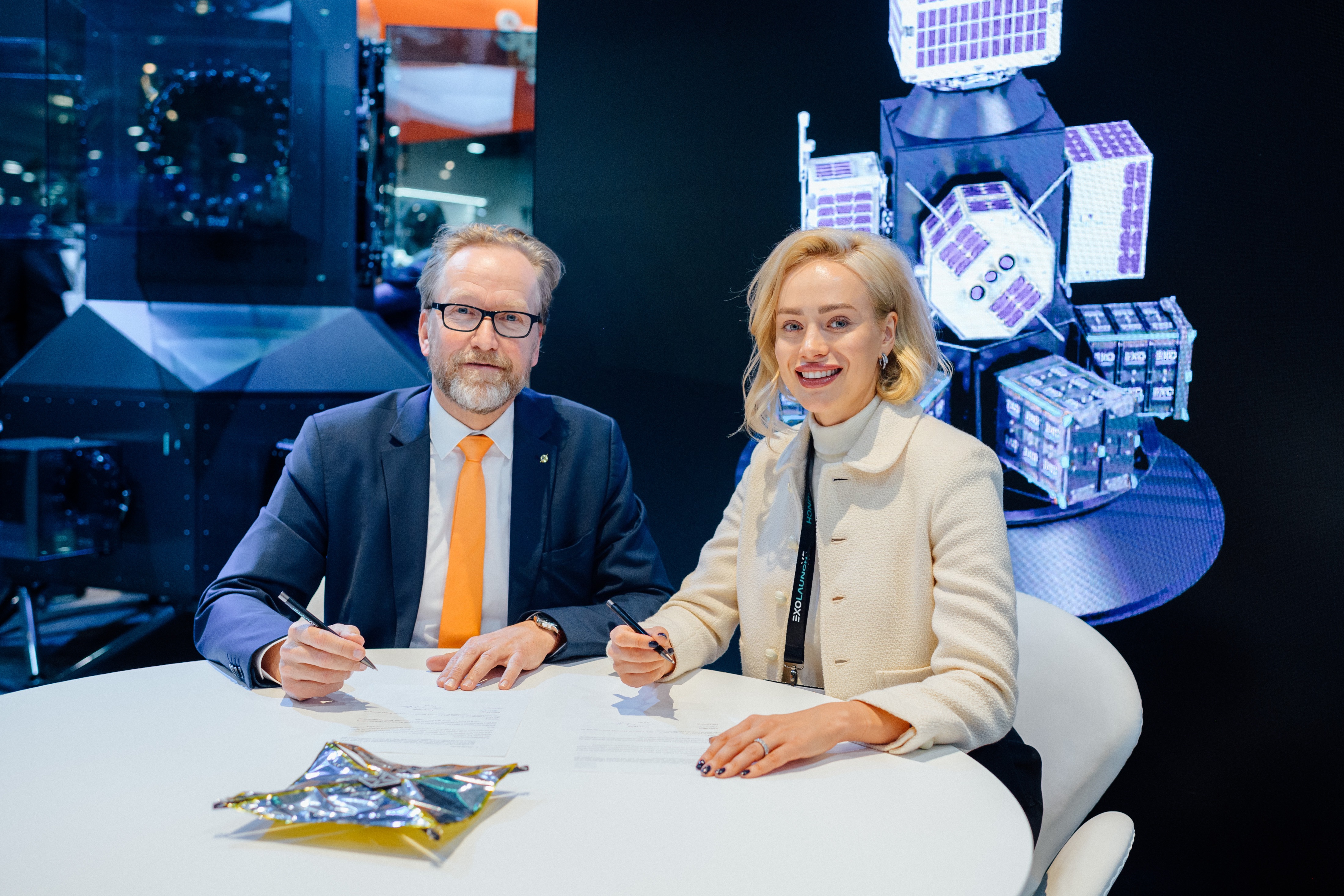
HPS is happy to join forces with the Germany-based Exolaunch and is fully engaged to support customers of Exolaunch by enabling this very special and successful NewSpace-launch service provider to grant priority access to the delivery schedule of flight-proven ADEO* deorbit sails which are currently in high demand.
EXOLAUNCH’s COO Jeanne Allarie and HPS’s CEO Ernst Pfeiffer signed an Agreement on Space Tech Expo 2024 in Bremen in a great joint spirit (see pictures) the ambitious endeavour of
See for the respective EXOLAUNCH announcement
(* ADEO-modules are needed to allow a satellite deorbit after its “End-of-Business” within five years; satellites without this or any kind of deorbit accelerator do not get clearance for launch anymore.)



November 2024
German space agency chief Dr. Walther Pelzer and DLR delegation focus on visit to HPS Group
During the traditional DLR delegation round on the opening day of the Space Tech Expo in Bremen, the head of the German Space Agency at DLR, Dr. Walther Pelzer, focused his attention on SMEs in the German space industry. Special attention was paid to the innovation forge HPS. And it was represented in groups: with HPS Germany (Munich), HPS Romania (Bucharest) and the joint venture company HPtex (Münchberg, Germany).
With reference to pioneering antenna projects such as HERA and EUCLID, company boss Ernst K. Pfeiffer emphasized the leading position Germany has gained in special antennas for space missions. HPS is also positioning itself as a leader in the commercial sector with the successful ADEO braking sail project, which ensures compliance with the new 5-year rule for satellite deorbiting and thus keeps the satellites ready for launch.
In his role as spokesman for German space SMEs, Ernst Pfeiffer also took this opportunity to emphasize the enormous importance of the DLR and ESA’s capability-enhancing technology programmes for SMEs as the innovation backbone of the industry. According to Pfeiffer, the precise promotion of the technological capabilities of SMEs via dedicated competition areas reserved for SMEs is irreplaceable.
Live demonstrations, e.g. of a functional model of the ADEO brake sail or a scaled model of a deployable large antenna reflector, supplemented by product demonstrations from HPS-Romania (e.g. radiator) and from HPtex’s MESH production (e.g. Ka-band mesh sample for use in the Copernicus mission CIMR) rounded off the visit program.
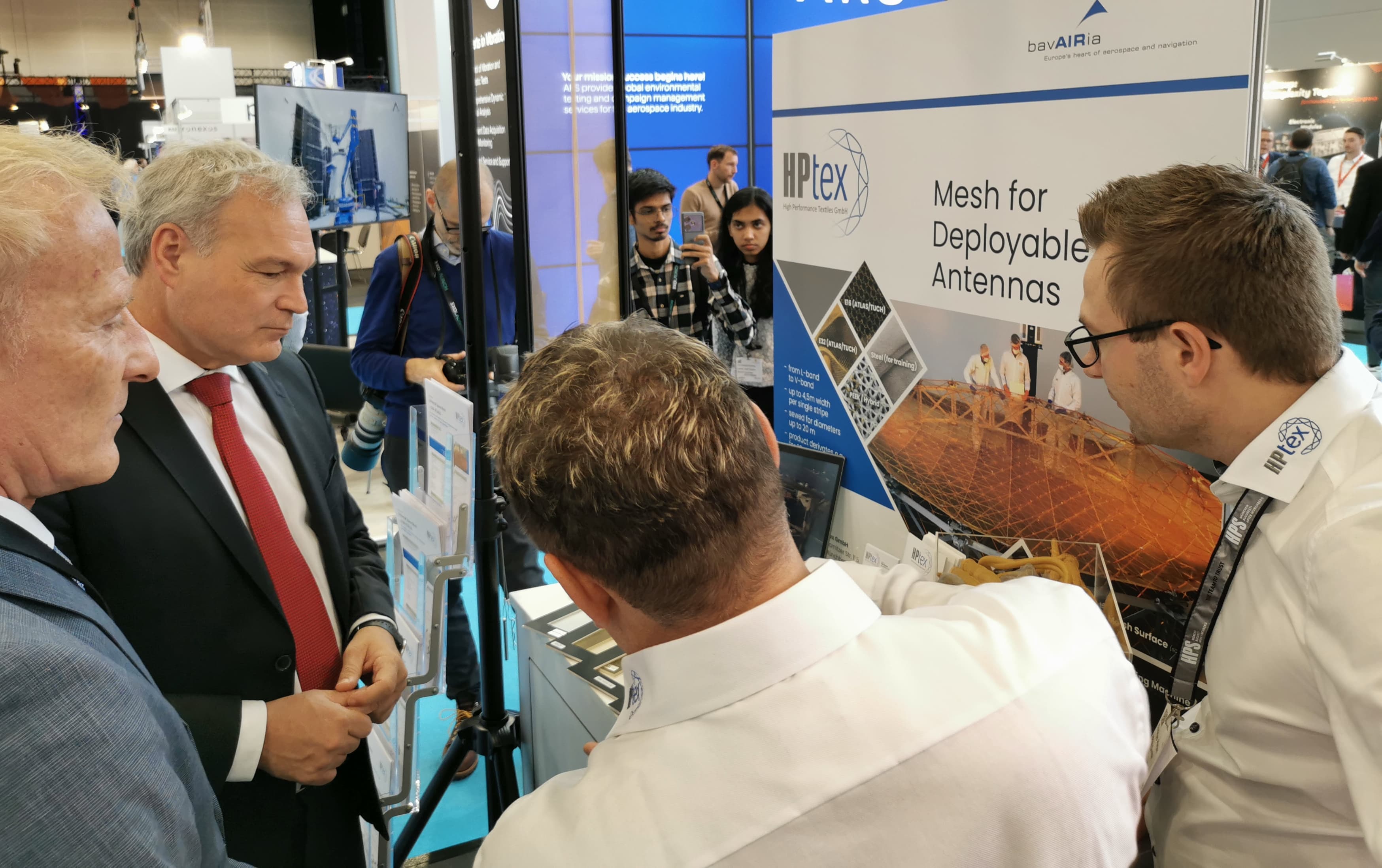



November 2024
New laboratory for mesh research at HPS
The Munich-based space technology company HPS is a joint venture partner of Iprotex-GmbH; both are equally involved in the joint company HPTEX in Münchberg near Bayreuth. This is where the flexible reflector material “MESH” is tailor-made and of the highest consistent quality for applications such as small and large deployable space antennas.
The market for mesh is divided among a small number of players worldwide. To survive here, continuous development is an essential prerequisite. HPS has therefore recently set up its own mesh research laboratory at its Munich headquarters on Hofmannstrasse. The initial team of two specialists is currently being expanded to include a further engineering position. The initial equipment of the laboratory for the further development and optimization of HPTEX mesh has already cost HPS 50,000 euros; among other things, investments were made in a mesh tension jig (stretch test rig) including an HD camera system. In addition, for yet another 50k euros the whole basement-area of the HPS building has been improved to host capacities for assembly work on ADEO brakesails in serial production.
Customized service is a top priority at HPS, so the new laboratory also carries out contract research, e.g. in a project called VMESH, in which a mesh for the very high frequencies in the V-band is being developed. The laboratory’s ability to carry out multiple iterated processes to measure the stretchability of antenna meshes is also unique on the market.
In addition, HPS is Europe’s only supplier of large deployable antenna subsystems with its own mesh production. The company’s flagship project is the ESA Copernicus Mission CIMR. HPTEX also serves customers from all over the world, including Europe, the USA, the United Arab Emirates, South Korea, Singapore and Taiwan, with the support of the new laboratory at HPS. The mesh is manufactured at HPTEX itself.
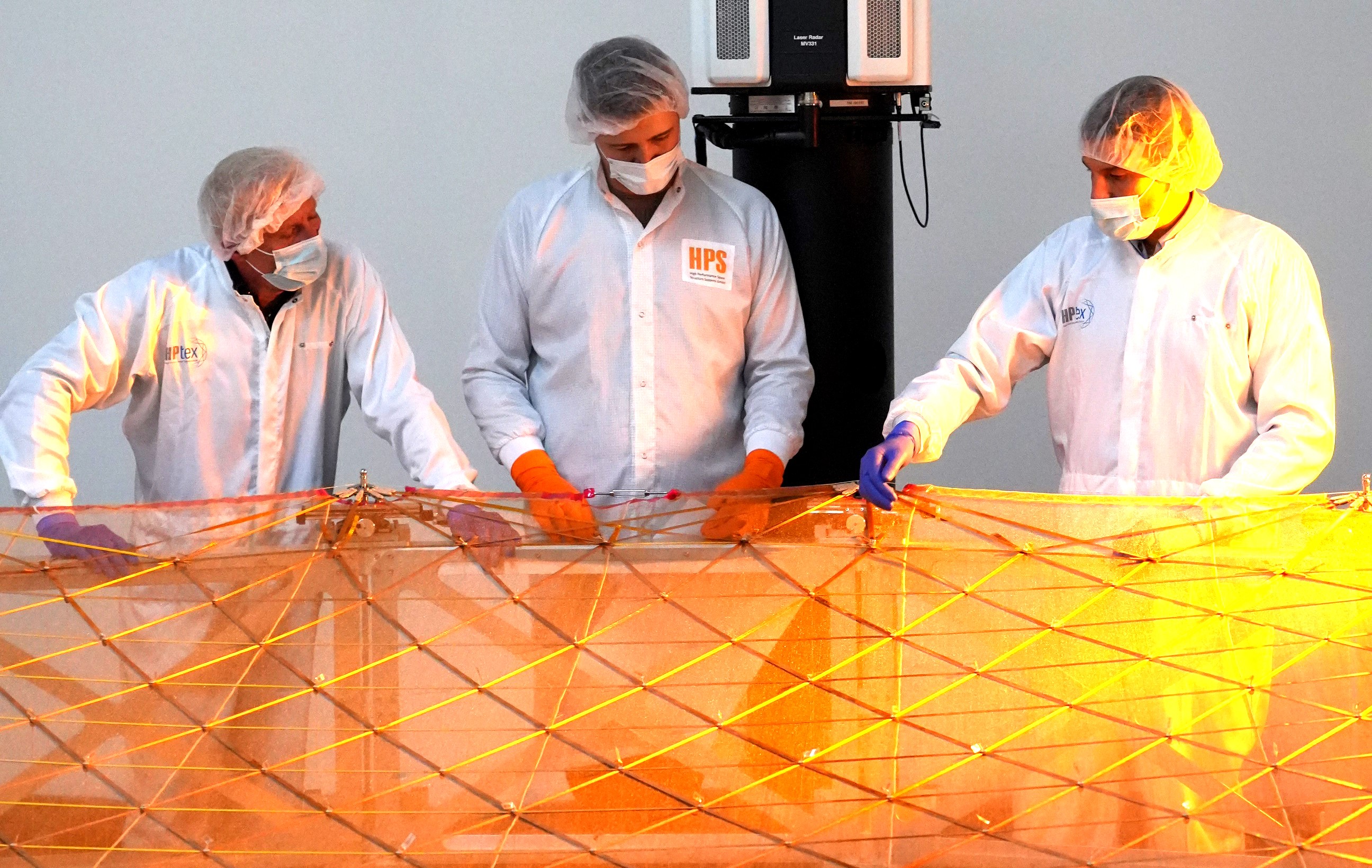


Oktober 2024
HPS Prominently Present at the IAC in Milano
Participating in the International Astronautical Congress, IAC, has developed into a good tradition at HPS over many years. This year, the company will be represented by Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO, together with ADEO project manager Mrs. Dorittya Milankowitch from HPS Munich and Horatiu Gheorghe as IAC-contact point for HPS Bucharest with products like secondary structures, thermal hardware and purging equipment. The HPS-team will keep up full presence during all five days of this international event.
Special highlights will be the company presentations; they are going to take place on Friday, 18th, from 10.15 to 10.45 a.m., and also as part of the Company Slam at the booth of the German association BDLI on Tuesday from 13.15 to 13.45 p.m..
Focus of both presentations will be on the product family of the ADEO deorbit sailsystem for automatic disposal of satellites after their end of mission, serving the idea of clean space, sustainability and debris avoidance even from the beginning of the satellite´s journey.
Main products besides ADEO to be asked at our booth: reflector antennas, deployable antennas, large deployable reflector subsystems, mesh, thermal hardware, purging equipment. HPS will warmly welcome there all its customers from both worlds: classic and NewSpace. For a dedicated prearranged business meeting please send a message to Contact@hps-gmbh.com.


Oktober 2024
Innovative BANT-1 reflector antenna from HPS for Reflex: exemplary symbiosis of NewSpace and established space-SME
NewSpace – this means, among other things, speed in development, production and provision, paired with innovative versatility as a leitmotif for the performance of the product. A current example of this is the broadband reflector antenna developed for the new Reflex Aerospace satellite by space SME HPS GmbH (Munich, Germany) with a broadband spiral as an axial feed. The primary development goal was to achieve a large bandwidth and considerable gain while at the same time limiting the time from order to delivery to the customer to just 12 months. The antenna consists of a prime focus reflector with a diameter of 700 mm and an f/D ratio of 0.32, which is fed by a compact ultra-wideband cavity-backed spiral (CBS).
HPS thus succeeded in meeting all customer expectations in terms of performance, price, and timing while adhering to best practices and strict quality management; the project can serve as a striking example of an exemplary symbiosis between NewSpace and established space SMEs towards “NextSpace”.
The Reflex satellite will be launched on board a Falcon9 as part of a SpaceX rideshare 12 mission.
Picture:
Satellite “SIGI” by REFLEX AEROSPACE with integrated reflector Antenna “BANT”, supplied by HPS Munich, ready for transport to the launchpad in the U.S. (left: Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO HPS, right:Walter Ballheimer, CEO REFLEX AEROSPACE, visit as of September 30th, 2024)

September 2024
ADEO Pico: The smallest dragsail gains a foothold in the largest market
Deorbit Technology from HPS
With the ink now drying under the contract for a PICO-class satellite deorbit device from the ADEO dragsail family of HPS, the Munich-based space technology company is now also setting foot on North American soil: After careful consideration of the alternatives, the Canadian company StarSpec Technologies decided in favor of the system for integration on their InspireSAT 12U ADCS MVP satellite, to be launched in 2026.
The ADEO-P was purchased at the beginning of July. The integration will be carried out by the experts in 2025. The satellite is planned to be launched in 2026 aboard a Falcon9 as part of the Transporter-17 SmallSat Rideshire mission from the Vandenburg Space Force Base in the USA. At the end of the mission, the dragsail will be deployed to a size of 1.4 m2 and automatically dispose of the satellite within the now obligatory period of less than five years. The satellite will burn up in the atmosphere without leaving any residue.
This initiative promotes StarSpec’s high precision space-qualified ADCS components, including sub-arcsecond precision star cameras, cogless reaction wheels, and ultra-high-bandwidth controllers, providing 100x the precision and imaging quality for LEO imaging satellite.
Jason Brown, Mechanical & Technology Lead, commented on the key factors leading to the selection of the ADEO-P for InspireSAT: “A primary mandate of InspireSAT is to provide high performance in-orbit capabilities in a way that does not compromise and strongly maintains the continued and future utility of LEO. We are delighted to have HPS, a proven high-tech specialist in the international space industry, at our side, allowing StarSpec Technologies to maintain its sustainable and orbit-conscious approach to space in a way that maintains focus on the successful demonstration of our transformative state-of-the-art ADCS. Thanks HPS!”

August 2024
ESA: 1 million for product innovation by HPS, AAC and DLR
ESA’s GSTP program is one of the European Space Agency’s most important instruments for promoting new technologies, particularly those generated by SMEs. The program also enjoys high priority in the overall ESA portfolio at the German space agency; the corresponding financial resources now also enable the launch of a new sub-program called “Product Initiative”. With the signing of the contract on August 7, 2024, ESA and HPS as the main contractor gave the go-ahead for the first technology project in this category.
It took just over six months from the idea to the signing of the contract; the funding amount is one million euros. The Munich-based space technology company HPS and its long-standing partner, Vienna-based Aerospace & Advanced Composites GmbH, are contributing 20 percent of their own funds, while the DLR Institute of Space Systems in Bremen is also on board on the research side. Over the next 24 months, highly innovative films (working name “ProFilm”) will be developed in various thicknesses and surface configurations and for large-area applications, which are characterized by two special features in particular:
In addition to use as thermal insulation for satellites, this also results in innovative applications as invisible brake sails as a further development of the HPS ADEO product range for deorbiting decommissioned satellites.
In this way, they serve four strategic goals of European space:
The ideas go as far as deployable structures that could make entire satellites invisible with ProFilm.
HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer is enthusiastic about the start of the project: “The innovation processes that have now been initiated will result in highly exciting products – the cooperation with our partners, DLR in the north and AAC GmbH in the south, alone is a guarantee of this. Above all, however, this premiere of ESA’s new GSTP sub-programme shows how quickly and effectively the European space agency can identify, accept and master technical challenges. This is exactly what European space travel needs, and this is exactly what innovation drivers from the ranks of SMEs need in particular.”

July 2024
Family & Friends Team Event at HPS Munich
HPS celebrates “Family & Friends”: July 10, 2024 is a special date – we celebrated with the entire HPS workforce and their families and all those many friends of our company according to the motto: Shared joy is double the joy.
Because we at HPS have many reasons to be happy: Since July 1, 2024, our HPS family has grown to a new record level with a total of 93 employees (including 11 freelancers and students) at the Bucharest (HPS Romania), Münchberg (HPtex) and Munich (HPS HQ) locations, and in Munich we have just expanded with a new, large floor in Hofmannstrasse as well as a large assembly area in the basement.
The circle of our friends from joint projects and association activities is huge, many from the Munich area came to visit us today, we were overwhelmed by the large number of surprise guests. Success is best celebrated with “Family & Friends”!

June 2024
ESA Leads the Way: Rapid Implementation of the Zero Debris Charter
Sustainability in space travel has also been an issue for the European Space Agency ESA for years. However, only a few months passed between the decision to adopt a Zero Debris Charter and its implementation.
Keynote speaker ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher also saw this as a sign that the time is finally ripe for concrete steps instead of pure symbolism, especially as ESA itself has provided significant impetus for the development of the two main technologies on the way to “Zero Debris”: firstly, ways of removing scrap from space, but above all, equipping satellites with deorbit technology from the outset so that no more waste is produced after the end of the mission.

ADEO Drag Sail: The Key to Sustainable Spaceflight
The ADEO brake sail, which is now available as an entire product family for all sizes of LEO satellites from HPS series production, stands for this. In addition to grants and support from ESA, DLR and Bavaria, HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer also invested a lot of the company’s own money in the project, always firmly convinced that the hour of ADEO would come sooner or later – and if a little later, then all the more powerfully.
It was exactly the same when, in mid-2023, the ESA set the new rule of a deorbit maximum of 5 years for ESA-funded missions instead of the previous 25 years, and, accordingly, LEO satellites without ADEO (or similar) will no longer be launched at all from October 2024, as SpaceX, for example, makes clear in its conditions of carriage in accordance with FCC regulations.
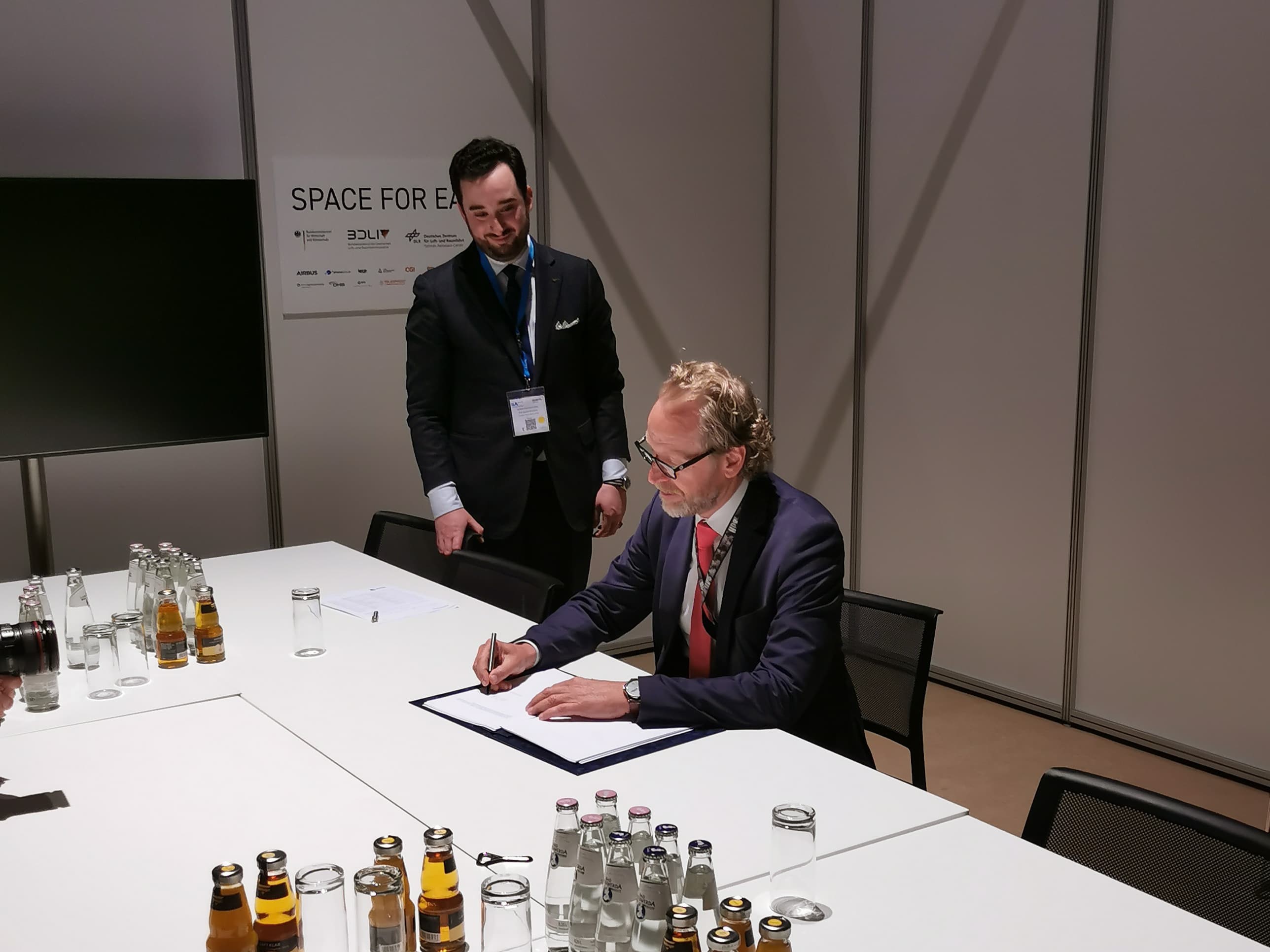

Historic Moment: 12 Nations Sign the Zero Debris Charter
The Charter was signed in Brussels on May 22 by 12 countries, including Germany. Since then, over 100 organizations, companies and entrepreneurs have been waiting for their cue to sign.
The ILA 2024 marks a very important stage on this path towards the sustainability of European space travel and sets an example for companies on other continents.

Dezember 2023
HPS completes the ADEO sail fleet with its first largest version under the version named L1. Its 25 square meters of sail area unfolded successfully deployed on Monday, 4th of December 2023 in a final ground test after a complete completed PFM qualification campaign. This included vibration tests in all axes as well as tests under thermal vacuum, including hot and cold firing tests (tests to verify the deployment release mechanisms under extreme temperatures). The tests were carried out under responsibility of HPS Munich at the facilities of the DLR Institute of Space Systems in Bremen – a prime example of cooperation between industry and research & development. This final and most important test enjoyed great interest from the media (including SAT1, RTL, NTV, DPA) covering the 20-minute deflation process and interviewing the enthusiastic project team of HPS and DLR. Links to the articles and television videos can be found HERE.
This test is also a success of ESA’s GSTP program, which significantly supported the development of ADEO-L1 financially and technically. Technology programs in general are essential for independent SMEs in the space industry and their products on the way to market readiness and worldwide series sales.
The ADEO brake sails deploy after the end of the satellite’s mission and brace themselves against the resistance of the atmosphere that still prevails in orbits up to an altitude of just under one thousand kilometers. This deployment immediately leads to a drastic reduction of the speed of the satellite and the entire package sets off on its accelerated descent towards the earth’s atmosphere, where it then burns up in the frictional heat of up to two thousand degrees Celsius. The entire return process takes even significantly less time than the latest guidelines prescribe. Until recently, the process could take up to twenty-five years, while it must now be completed within five years. And, to ensure that operators follow the rules, launch service providers such as SpaceX no longer even take satellites into space if they are not equipped with the appropriate return technology from the outset.
The Munich-based space-tech company HPS had this development in mind more than ten years ago, when no one else was really thinking about ways to avoid space debris. With great support from the space agencies ESA and DLR, the DLR institutes in Bremen and Braunschweig, the companies DSI, Bremen, and formerly HTS, Coswig, plus a seven-digit-investment of HPS, the company´s highly committed young team of experts has created an entire product family under the generic name ADEO, from the smallest versions ADEO-P (Pico), ADEO-C (Cube) and ADEO-N(Nano), ADEO-M (Medium) and the latest member of the group, ADEO-L (Large). The development master plan not only extends even further to possible ADEO variants with up to 100 square meters of braking surface, but also leaves enough room for derivatives with completely different applications, such as the monitoring of space debris smaller than1 cm directly in space.
In its largest flight-ready version to date, L1, ADEO has a take-off weight of 10 kg at dimensions of 43 cm x 43 cm x 25 cm; in contrast to the smaller versions, this unit also requires its own power supply for motor-controlled deployment of the masts and sails. ADEO-L1 generally fits perfectly on satellites up to the 1,500 kilo class.
In the first quarter of next year, ADEO-L1 will be integrated onto a satellite of the Belgian company Redwire for its first test flight at the end of 2024/beginning of 2025 as part of a EU program, while the versions ADEO-N1 and ADEO-N2 have already passed their baptism of fire in space. Approaching the fiery finale is currently ADEO-N2, deployed in December 2022. Since then, it has already lowered its satellite from an orbital altitude of 510 km to 460 kilometers in only 12 months without the aid of any fuel or attitude control. Expected “arrival” in a completely burnt-up state: mid2025 – and thus even around five times faster than without sails and twice as fast as prescribed.
ADEO-L1 will master this path of final in-orbit verification just as safely, company boss Dr.-Ing. Ernst K. Pfeiffer is certain. As with the other versions, it will then go straight into series production for which the company has special production facilities at its Munich and Bucharest sites.
November 2023
As part of the National Program for Space and Innovation and based on the decision of the Budget Committee in November 2022, the German Space Agency launched a competition for promising space innovations. The winner can expect a fully organized and financed demonstration flight with launch by 31.12.2025. On Thursday, 23 November 2023, the Federal Government’s Space Coordinator, Dr Anna Christmann, selected Munich-based space technology company HPS as the winner of the competition in the small satellite payload category with its ADEO-Cube space sail version at the 2023 Small Satellite Conference. The ADEO product family is designed as a series with different model types (Pico, Cube, Nano, Medium, Large), with which all satellites from the Cubesats to the larger representatives with 1.5 tons (class “M”) are automatically removed from low Earth orbit (LEO) and disposed of at the end of the mission. This so-called “deorbiting” with the ADEO braking sail not only fulfills, but even undercuts the maximum duration of 5 years that will apply from October 2024 instead of the 25-year guideline that has been in place since the 1960s. Quite simply, this means that no satellite will soon be accepted for launch without special on-board technology, such as the appropriate space sail from HPS’s ADEO series, if it cannot otherwise be legally disposed of. Since SpaceX, for example, as the leading launch service provider, will be introducing this rule from October 2024, it will apply to practically all future satellites, including those that are already in the design and manufacturing phase today.
As HPS CEO Ernst K.Pfeiffer, there is still only one alternative to ADEO, but it “is chemical, expensive and – in the case of a damaged satellite – inoperable”, the passionate aerospace engineer states about the market position of the ADEO space sail: “ADEO is currently the cheapest, most reliable and cleanest solution for legal deorbiting on the global market, available in all classes thanks to series production at HPS Bucharest and HPS Munich, and highly competitive in the hotly contested commercial market for satellite technology.We at HPS, especially our development team, are all very pleased that our sustainable technology has been recognized by the Small Satellite Competition at the highest level.”

November 2023
Initiated by ESA´s office for “Strategy and Transformation” a considerable group of European space companies, including HPS, got together in order to jointly draft and now implement this continent´s set of rules for sustainable use of space. HPS is one of the first companies to sign the document on November 7th, 2023. Though legally non-binding, the “Zero Debris Charter” aims at putting an end to the inconsiderate and irresponsible pollution of space with tech-junk. In detail, the Charter clearly names the following targets:
Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS at the signature ceremony: “In our days now space is rapidly developing into the most important resource for the implementation of new technologies shaping our future on Earth. All efforts to preserve space from the beginning are therefore nothing less than efforts to preserve the fundamental conditions of life and its prosperity for humankind´s generations to come.”
*For more see:
*https://esoc.esa.int/zero-debris-community-update
*https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Clean_Space/World-first_Zero_Debris_Charter_goes_live
*https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Clean_Space/ESA_s_Zero_Debris_approach
*https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Clean_Space/The_Zero_Debris_Charter
November 2023
Less than 36 months ago, they were regarded by many as nothing more than political empty phrases: the “Green Deal” of the EU Commission in Brussels and the “National Orbital Debris Implementation Plan” of the White House in Washington. Satellites continued to be launched into near- and far-Earth orbits with the prospect of becoming junk and endangering other missions for a quarter of a century after they finally burned up in the atmosphere. But that’s over now: With the adoption of the “Zero Debris Charter”, ESA has committed itself on November 7, 2023 to taking steps towards total avoidance of any space debris from 2030 at the latest, and even more concretely, namely already from October 2024, SpaceX, with over one hundred launches per year the world’s most important launch service, will no longer transport any payloads that are not equipped for their disposal within a maximum of 5 years after the end of mission operations. And as early as 2023, the U.S. FCC (“Federal Communications Commission”), as the supervisory authority for the allocation of radio frequencies, sentenced a satellite operator to a fine of $150,000 for prolonging the operation of his satellite with the propellant actually reserved for disposal, thus recklessly endangering all other missions in the vicinity. While the sum might make some people smile, the FCC has now put an end to all symbolism with its decision to no longer grant radio licenses to satellites without on-board technology for return (technical term: “deorbit”) within 5 years of the end of operations. Under the double threat of operation AND launch ban, practically all operators are forced to equip new satellites only with guaranteed reliable deorbit technology from now on.
This can be done with the on-board propulsion system using chemical propellants while shortening mission and profit, but even that does not work in case of satellite failure and is also comparatively expensive due to the need for constant control monitoring from the ground.
The alternative is called ADEO: from HPS (Munich and Bukarest) a space sail, self-deploying at the end of the mission, which automatically removes the satellite from space well below the specified deorbit times, is ideally suited as baseline-tech and emergency parachute. Already 36 million flight kilometers before the planned maneuver, the German specialist for orbit guidance and collision avoidance OKAPI:Orbits (Braunschweig) as a cooperation partner calculates the point for the descent without risk for other satellites. In addition, HPS partner number two, the Italian company AVIOSONIC, in constant liaison with the worldwide air traffic control stations, ensures via new ADEO-features highly accurate position conrol and spares aircrafts from hits by any satellite parts that may not have burned up.
The ADEO product family with officially attributed highest possible level of reliability (“TRL 9”) holds tailor-made solutions for all satellites from the tiny Pico- and Cube-Sat up to the 1.5 tonner and for all low-Earth orbits up to a distance of 900 kilometers from Earth. All ADEO lines are mass-produced by HPS, yet they feature adaptive design for special requirements that may arise from satellite design.
The prices of all ADEO models without exception are considerably lower than the expenditures required for deorbiting with chemically driven engines – apart from the fact that the safety of the deorbit of even these satellites – for example in the event of a system failure – can actually only be guaranteed by an ADEO system carried along as a backup.
For more detailed information on ADEO see: https://www.hps-gmbh.com/en/portfolio/adeo-angel-on-wings/
June 2023
When, after two, five or more years of operation, a satellite is supposed to leave its orbit and re-enter Earth, it’s a ride on the skyway to hell in two respects: first, for the satellite which is destined to burn up in the atmosphere, but also for other satellites as well as for an encounter with scrap parts that could hit it like unguided missiles – and produce even more junk. Satellites equipped with the ADEO braking sail from HPS are already in automatic descent mode. From now on, however, this can be upgraded by the Collision Avoidance system from industry-leading German startup OKAPI:Orbits. The company emerged as a spinoff from Braunschweig University of Technology in 2018 after over 40 years of intensive research. This Collision Avoidance System minimizes the collision risk during the de-orbit trajectory by figuring out the situation even ten days in advance. Appropriate maneuvers are also recommended for the satellite’s control system. This is made possible by the unique AI behind OKAPI:Orbits.
“Picture a distant view of 6.72 million kilometers of orbits on which about 10,000 satellites, 1,000,000 large and medium objects and 130,000,000 small ones exist that are not currently trackable. This is how complex computing operations is. Now, we should also take into account their velocity of 20,000 to 30,000 kilometers per hour. To any human sensibility, this is pure chaos, which the artificial intelligence behind our Collision Avoidance Software handles with aplomb,” says OKAPI’s company CEO Kristina Nikolaus.
Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS, a medium-sized innovation company, adds, “Our ADEO braking system not only performs the fastest possible passive descent even under adverse conditions – for example, when the satellite is already dead – it is also the deorbit solution with the largest safety reserve directly on board. Customers who don’t want to rely solely on their own software to control their satellites will find a unique safety architecture for the deorbit of almost all satellites with ADEO’s optional assistance systems for position tracking (Aviosonic) and optimal descent prediction (OKAPI:Orbits) at HPS.” ADEO is under discussion as a deorbit subsystem for the satellites of Europe’s coming constellation IRIS2 and “together with the features of Aviosonic and OKAPI:Orbits it levers the constellation to the most secure and sustainable one also after satellites’ nominal lifetime.”
During descent, the combination of all three technologies onboard the satellites will increase significantly the orbit determination and prediction, which is a unique advantage also for other satellites, constellations and stakeholders like owners, operators, and insurers.

Mai 2022
(Munich-Milano, May 10th, 2023). At testified TRL-9 and with solid flight heritage the sail system “ADEO” already is the leading device for quickly deorbiting almost all satellites, thus preventing spacecrafts after their end of mission from becoming as well as producing new space junk for years to come. Because it is a sail, it does not produce any pollution itself, chemical or otherwise, and because this very sail will be in its next version also transparent and absolutely non-reflective, it does not cause any irritations to any space observer on earth. Munich based spacetech innovator HPS, a medium sized company with a subsidiary in Romania and a total headcount of 80, has invested – together with several institutional and industrial partners – 12 years of constant development and qualifying into ADEO, and is now ready to take yet another giant leap by joining innovative forces with Aviosonic Space Tech, Milan/Italy.
Aviosonic Space Tech, born in 2015, owns the patented DeCAS system (Debris Collision Alert System) for in-orbit/de-orbit tracking and re-entry footprint prediction of space vehicles. DeCAS is a 1U mm system which always maintains a constant link with the ground operation center allowing precise information on the satellite position, aliong with the calculation of the re-entry footprint in real time, with the aim of collision avoidance between satellites, satellites and aircrafts as well as to alert government agencies. The technical characteristics and modularity allow DeCAS to be installed on any space vehicle, offering different services depending on the mission requirements. DeCAS, which took part in different space missions, provides a unique service for satellite tracking, decommissioning and re-entry prediction in real-time.
Prof. Piermarco Martegani, CEO of Aviosonic Space Tech says:”The integration between DeCAS and ADEO allows the creation of a unique product on the market capable of strongly implementing the safety of space operations both during orbital and decommissioning re-entry phses, even in the event of failure of the hosting satellite. This safety information is also needed by the Air Traffic Management System. The collaboration between Aviosonic Space Tech and HPS is the demonstration that in order to guarantee safety during space operations, an international cooperation between SMEs is necessary.”
HPS-CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer shows bulletproof confidence in the future of ADEO on the world market and emphasizes: “ADEO has all the facts on its side: first, all space industry badly needs a deorbit device like ADEO, since the faster the sail opens free orbit positions, the longer we can keep space as a sustainable surrounding. And, from second to infinite: ADEO combines TRL9 and flight heritage, offers a comprehensive range of models, beats economically as well as ecologically any other type of deorbit device, also it is already in serial production at HPS. And now we even join forces with the two outstanding innovators in their fields, and others will join, underlining once again what´s at the core of ADEO: 100 percent European, 100 percent SME, 100 percent sustainability in space – and exactly what Europe wants for Iris2.”
Contact for further information:
HPS: Dr. Daniel Stelzl, stelzl@hps-gmbh.com
Aviosonic: Prof. Piermarco Martegani, Piermarco.Martegani@aviosonic.it
ADEO Dossier: German: (https://www.hps-gmbh.com/tag/adeo/)
ADEO Dossier: English: (https://www.hps-gmbh.com/en/tag/adeo-en/)
Video: https://youtu.be/pUeSZzdn_6c
April 2023
After FCC, SpaceX, and ESA now also the three German startups racing for the smaller launchers` pole position in the commercial market made it clear that tickets to space will be available only to satellites prepared to be able to deorbit quickly after service.
The companies made their points recently in statements to the German space magazine “Raumfahrt Concret”.
For more details see: RCI-Newsletter-1-2023.pdf (hps-gmbh.com)
Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of HPS, the German spacetech company that has developed ADEO to become the number 1 deorbit device for spacecrafts on the market, comments: “While we witness many cases of exorbitant differences in opinions when it comes to principles the space industry should follow, it is with great relief that we see this case ruled by unanimous voices echoing the new green spirit of deorbit from everywhere.”

January 2023
Already in the heat of last summer, HPS in Munich was preparing for the third mission of the innovative space brake sail ADEO-N, which unfolds automatically at the end of the mission and drives “its” satellite into the atmosphere to burn up. This technology avoids the formation of new space debris already on the ground and finally makes space missions sustainable.
The ION Satellite Carrier with ADEO-N3 with its sail area of 5sqm has been on board a Falcon 9 since the picture book start on January, 31, 2023 from spaceport Vandenberg, California, now on the way to the target orbit at 270 to 500 km altitude at 53 degrees inclination. Probably by the end of 2023 ADEO-N3 will then, as on previous flights – including one with ION also on Falcon 9 – deploy the braking parachute and remove its ION Satellite Carrier from orbit without leaving any residue many times faster than usual. With the flight heritage accumulated by then, the mature ADEO system heralds a “green” space age. Because at least for European missions or missions from Europe, there will – in all probability – no longer be any more launches without deorbit tech on board: The Green Deal of the EU will then also apply to “clean-green missions” in space.
On the current flight, ADEO-N3 acts as another verification of maturity for HPS. D-Orbit and HPS already captured what will happen high above the earth during a nominal mission as historical testimony on video during the last flight:
https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7021106640993021952
Video is free for publication
The attached video, recorded directly on site with the on-board camera of the ION satellite of the Italian cooperation partner D-Orbit, provides live proof: with the product of HPS, which is now ready for series production after twelve years of development with great support from ESA, DLR and the Bavarian government, a new era of responsibility in space is beginning. ADEO is manufactured in series by HPS at its sites in Munich and Bucharest, primarily for constellation satellites. ADEO products are available for satellites weighing up to 2,500 kilograms at flight altitudes of up to 800 km. Even higher-flying satellites can be operated with ADEO if they have previously lowered their orbit accordingly using their own propulsion. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “With ADEO on board, satellites do not become space junk in the first place. And at conditions that are ALWAYS more economical than all other options.”
January 2023
On December 15, 2022, at 12:10 UTC, the world’s unique ADEO braking sail from the German space technology company HPS GmbH, Munich, opened the chapter of sustainability for international spaceflight 500 kilometers above the Earth: as planned, on time and precisely, the sail attached to the ION SCV 003 satellite unfurled over an area of 3.6 square meters to remove “its” satellite from orbit in the shortest possible time without leaving any residue, thus avoiding hazards for other space vehicles and making room for the next generation of satellites at its former orbital position. Preliminary studies and calculations indicate that this will reduce the descent time not by half, as originally expected, but rather by as much as five times.
The attached video, recorded directly on site with the on-board camera of the ION satellite of the Italian cooperation partner D-Orbit, provides live proof: with the product of HPS, which is now ready for series production after twelve years of development with great support from ESA, DLR and the Bavarian government, a new era of responsibility in space is beginning. ADEO is manufactured in series by HPS at its sites in Munich and Bucharest, primarily for constellation satellites. ADEO products are available for satellites weighing up to 2,500 kilograms at flight altitudes of up to 800 km. Even higher-flying satellites can be operated with ADEO if they have previously lowered their orbit accordingly using their own propulsion. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “With ADEO on board, satellites do not become space junk in the first place. And at conditions that are ALWAYS more economical than all other options.”
December 2022
For 16 months now, an ION satellite carrier of the Italian service provider for unmanned space transportation D-Orbit has been orbiting the Earth in low orbit. Launched by a Falcon 9 on June 30th 2021, it has only one last task after the mission launch of the high-tech passengers from eleven countries: to sail gently as if on “angel wings” to the edge of the Earth’s atmosphere in the shortest possible time with the help of the autonomous braking sail ADEO from the Munich-based space company HPS and to burn up there without leaving any residue.
The test model is the smallest variant of the ADEO product family with a weight of 800 grams, a packing size of 10x10x10 cm and an unfolded sail area of 3.6 square meters. This ADEO-mission “Show me your Wings” is now the final proof-of-concept in a series that also included a first flight with Rocket Lab’s Electron in 2018 and several parabolic flights from 2019 to 2022.
After the end of this nominal ION mission called “Wild Ride”, ADEO’s decelerator sail now deployed in front of the “eyes” of the integrated camera and immediately initiated descent (“deorbit”). ADEO completes deorbiting many years faster than the “unbraked” satellites currently still in widespread use and clears its operational position in orbit correspondingly earlier for a new satellite, which also prevents uncontrolled pollution of space by collision debris. In addition, ADEO helps extend the satellite’s uptime by allowing the sail to continue its descent even when the satellite is out of power and propulsion.
Incidentally, the time required for deorbiting is accurately measured so that it can be used for any necessary recalibration of the HPS deorbit timer. This is a globally unique computational program for predicting the deorbit times of all possible satellites with and without ADEO braking sails. The theoretically developed mathematical algorithms of the computer are thereby differentially refined by empirically obtained data from the field. The ADEO Deorbit Timer is a valuable service to HPS customers around the world.
Series production of the ADEO versions for all satellite classes with flight altitudes below 900 kilometers is in full swing at HPS in Munich (Germany) and Bucharest (Romania). The first companies, such as NewSpace startup Reflex Aerospace (Berlin and Munich), have already signed letters of intent to equip their entire future satellite fleet with ADEO or have announced that they will do so shortly. Others like BST, Berlin, are integrating ADEO as a standard option in their offerings to customers. An additional surge in demand was triggered in the fall of 2022 by the announcement by international policymakers that satellite deorbit times would be drastically shortened down to just 5 years due to the extreme increase in usage density on all orbits, and that corresponding additional equipment would be required by law.
The extremely sharp picture proof of the successful unfolding now opens a new chapter in the history of HPS, in addition HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer: “And again, a new chapter of programmatic success could be written, which is only possible through trusted space partnerships: research and development with institutes (like the Fraunhofer Institute in Freiburg and the DLR in Bremen) in the early and development stages, financial support from the Bavarian State and the German Space Agency, a vey strong engagement of ESA within its GSTP-program (without this support, including the people behind it, we would still be a long way off!!!), the extremely dedicated staff of my NewSpace team and finally with the people of the system companies, like D-Orbit, who finally, made possible to download from space the image of the unfolded sail, which is important for our next chapter. A great step for HPS, another step for sustainable spaceflight.”
ADEO – Contact: adeo@hps-gmbh.com
May 2022
Paris-Munich-Berlin, September 19th, 2022. Today satellite manufacturer Reflex Aerospace (Munich/Berlin) and space-tech company HPS (Munich), signed a letter of intent that will set the pace in striving for a sustainable use of space, through the prevention of space debris Reflex Aerospace is committed to removing all satellites from orbit after system end of life, and has chosen subsystem specialists HPS as its preferred partner to equip their satellites with ADEO sail-system as the deorbit system. The mission is clear, to ensure a safe and sustainable use of space for the foreseeable future. The two German Space players share a common goal in putting the European Commission´s “Green Deal”, ESA’s “Zero Debris Initiative” and the US “National Orbital Debris Implementation Plan” into practice.
The dragsail ADEO is available in three different versions, and covers all possible shapes and sizes of satellites active on orbital altitudes up to 900 kilometres. As a result, ADEO provides their system to over 90 percent of all constellations that are currently in planning. Partnering with ADEO underlines Reflex’s ambition to foster sustainability in space and responsive space capabilities, creating additional value for their satellites and subsequently for their customers. The first step and first integration of an ADEO dragsail will be the Reflex Demonstration Mission planned for mid 2024.
The CEOs of both companies signed the agreement today, Walter Ballheimer for Reflex, and Dr. Ernst K. Pfeiffer on behalf of HPS. Following the signature, Walter Ballheimer said, “We know the satellite manufacturing business for a long time, and from a mere business perspective one can understand that some of our competitors hesitate to invest in sustainability, if that affects rentability. Our view is, however, that this is short sighted and will inevitably lead to a situation where space endeavours become incredibly risky due to the amount of debris in the low earth orbit We don’t want to wait for this scenario to materialize, instead, we see it as a clear mandate for us and our customers to assume factual and ethical leadership in this matter.” Ernst Pfeiffer added: “Every breakthrough is a highly emotional moment, and this one now is certainly one of the most important ones in the history of our company. We started developing large deployable sail subsystems, originally with partners for the purpose of solar sailing ((i.e. DLR Institutes), back in the year 2000. It took over twenty years, uncountable hours of work done by the best engineers in the field, as well as sweat and tears when the project ran more than once into dangerous waters concerning its long-term financing. We are glad and thankful that over the decades we received so much support from people and institutions who never stopped believing in our final success. DLR and ESA have to be mentioned here in their role as most important strategic investors. This step together with Reflex Aerospace justifies the worthiness of all that effort and shows that ADEO will make its way as the central tool in keeping space save and sustainable.”
For more detailed information on ADEO see: https://www.hps-gmbh.com/en/portfolio/adeo-angel-on-wings/
For more detailed information on Reflex Aerospace see: https://www.reflexaerospace.com/
September 2022
UNIO Enterprise GmbH, THE European NEWSpace System house for satellite constellations made in Germany, founded by ISAR Aerospace, Mynaric, Reflex Aerospace and SES S.A has confirmed to equip all their European constellation satellites with the ADEO dragsail module: https://unio.global/.
ADEO will accelerate the decommission of the satellites and prevents space from getting polluted by debris even before it occurs.
We feel honored to have been selected as a partner for space sustainability by this meanwhile famous European NewSpace system house: To us at HPS, this is inspiration and motivation to carry on driving the idea of space sustainability to its technological extremes.

August 2022
Paris-Munich. August 1, 2022.
Just one last signature, and the success story of the almost decade-long development of the European deorbit sail ADEO by HPS is going to find its seamless continuation: the model ADEO M for medium satellites of 100-700 kilo weight on orbits up to 900 km altitude – so, typical representatives of the currently almost exponentially growing constellation projects – will be made fit for series production and distribution on the commercial market by the HPS Group in Germany and Romania.
Parallely, additional features of ADEO N (Nano) will be developed. ADEO M follows the versions ADEO N and ADEO L (Large), which have already been on the market for 1.5 years. With the third model, HPS now closes the last gap in its product portfolio and addresses in particular the booming NewSpace market thanks to maturity level TRL 9 and growing flight heritage on missions of various carriers with world-leading deorbit automatic.
This leadership is also a result of the steady and now renewed support from Europe’s GSTP technology program and its German SME initiative on the part of ESA and DLR Space Agency. “Everyone is talking about space debris; thanks also to ESA´s “Zero Debris Initiative”, with ADEO, our customers are making sure it doesn’t even happen.
This is the only way a clean-green mission works, the only way the EU’s Green Deal becomes a reality also in space.”
For each satellite on LEO there is a suitable ADEO, which accelerates deorbiting by a factor of about 20. All interested companies get the exact forecast free of charge and super fast; all they have to do is feed our globally unique “ADEO deorbit timer” with the data of their satellite and then let the algorithms do their jobs,” says HPS CEO Dr. Ernst K. Pfeiffer. As in the case of ADEO N and ADEO L, already now orders for new satellite projects are also being accepted for ADEO M, shortly before the start of series production, in order to harmonize planning and production processes on both the HPS and the customer sides.

July 2022
At the height of the summer vacations, HPS in Munich is at full power for the preparations for the third mission of the innovative ADEO space braking sail, which deploys automatically at the end of the mission and propels “its” satellite up to 20 times faster to burn in the atmosphere. This avoids pollution and makes space travel sustainable.
It will arrive in Italy as early as the end of August for assembly on the ION Satellite Carrier, D-Orbit’s orbital transfer vehicle (OTV). It is the ADEO-N version for small satellites with a sail area of 5 square meters.
Falcon 9 from SpaceX will be responsible for the transport into a mid-inclination orbit towards the end of 2022. With the flight heritage accumulated by the end of the year, ADEO will enter a new space age in 2023.
At least for European missions or missions from Europe, there will most likely be no more launches without deorbit technology on board:
The EU’s Green Deal then also applies to clean-green missions in space.
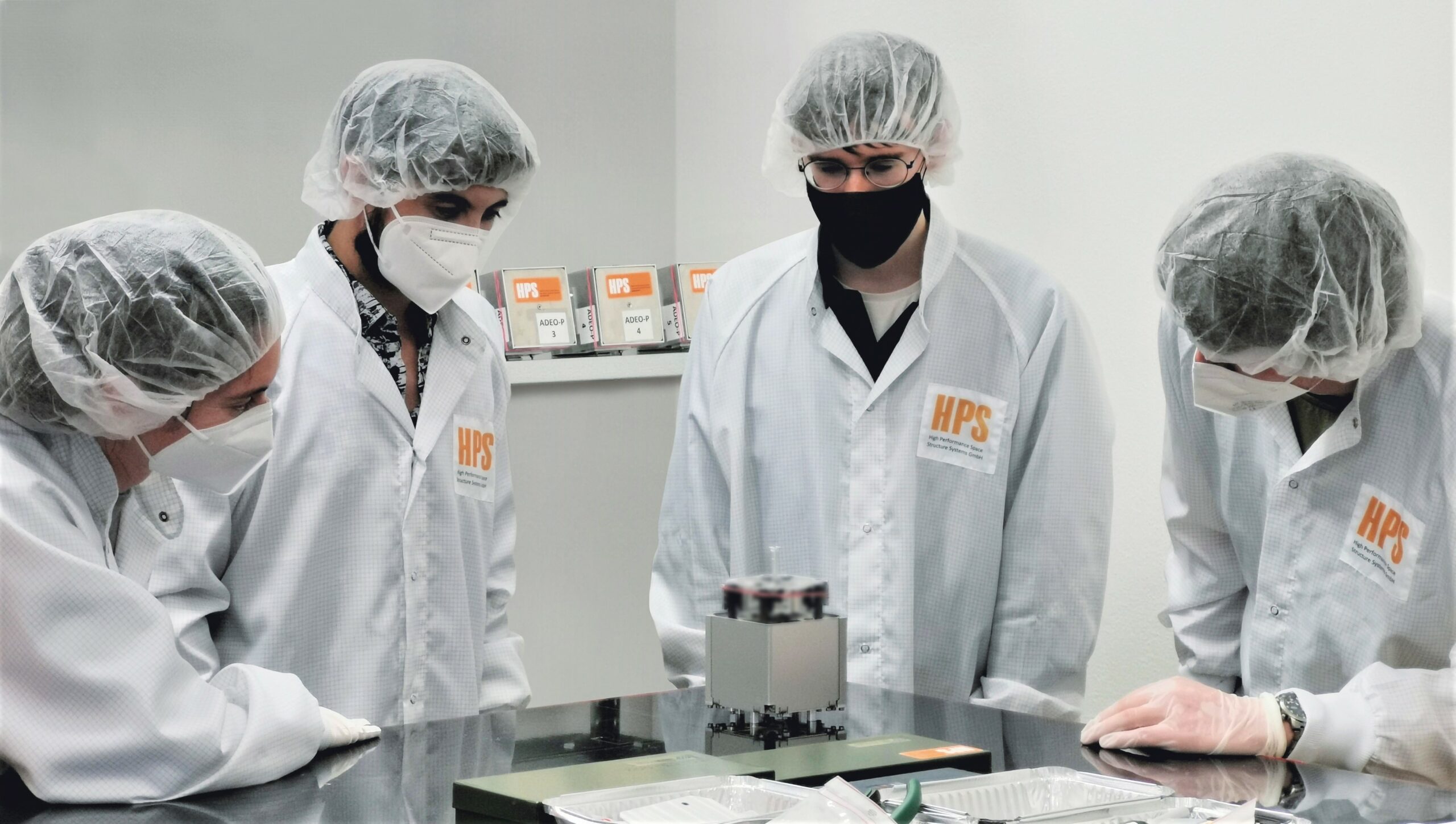

June 2022
Next milestone in commercializing ADEO dragsail for deorbit:
Reflex Aerospace (supplier of tailor made, high performance small satellite platforms) announces to use the automatic ADEO dragsail by HPS as standard deorbit device for their satellites. ADEO will guarantee a maximum deorbiting time of less than 5 years and contribute to Reflex Aerospace´s philosophy of responsible, sustainable and future-oriented space missions. Together we realize CleanGreen Space missions!
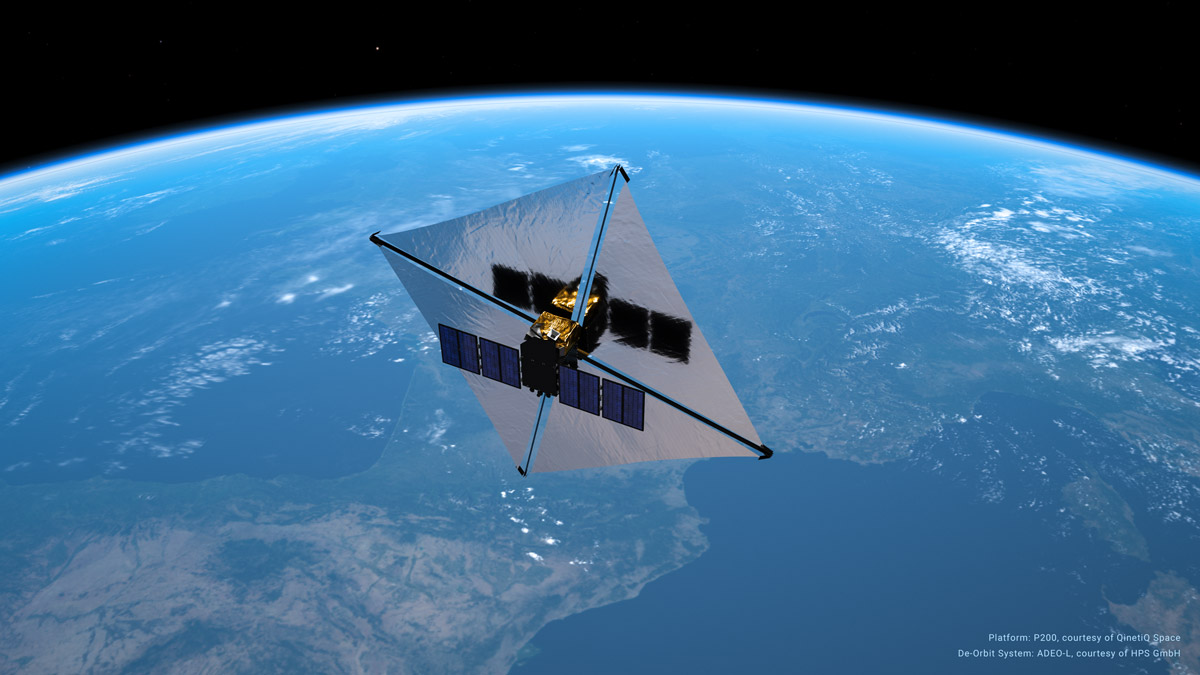

December 2021
By 2025, Europe will have its own constellation of satellites to ensure sovereign capacity for both commercial and institutional communication channels. Fast Internet, autonomous mobility at sea, on ground and in the air, automatic exchange of information between technical installations, support for military and humanitarian actions, and other applications for public authorities, companies, and citizens realised by a consortium formed by Reflex, laser specialist Mynaric and launch service provider Isar Aerospace.
The European Commission is also very interested in such a concentration of innovative forces and selected the UN:IO consortium for one of its two study tenders addressed to companies from the so-called “New Space” domain and endowed with 1.4 million euros. For the EU, a secure, very fast and, above all, sovereign communications network for Europe is a top priority. In addition, it must meet sustainability criteria for the EU’s “Green Deal” – and that is where ADEO comes in: The ADEO subsystem is a scalable, deployable drag augmentation device that uses the residual Earth atmosphere present in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) to passively de-orbit satellites between 1 to 1.500 kg. For the de-orbit manoeuvre, a large surface is deployed which multiplies the drag effect of the satellite´s surface significantly: The drag force is increased causing accelerated decay in orbit altitude. Advantageous about a drag augmentation device is that it does not require any active steering and can be designed for passive attitude stabilization, thereby making it also applicable for non-operational, tumbling spacecrafts. The passive ADEO subsystem requires neither extra propulsion nor engine, which makes it lighter in comparison to active subsystems.
So, after years of development, tests and zero-g- and in-orbit-verifications ADEO is now going to celebrate its world premiere as central element bringing sustainability to space on angel wings.

July 2021
On Wednesday, June 30, at 21.31 hrs CEST a Falcon 9 by Space X took off to a transporter 2-mission from legendary spaceport Cape Canaveral, Florida. On board: Italian NewSpace company D-Orbit´s ION Satellite Carrier on its „Wild Ride“-mission with tech-passengers from 11 countries, among that HPS’s ADEO-N2, named „Show me your Wings“. ION was successfully separated from the launcher exactly one hour after liftoff.
The ION-platform itself will now seperate one payload after the other on their respective orbits for in-orbit validation tests, until finally the platform turns into a test object itself, since it will be brought back „home“ by ADEO, the world’s only industrial NewSpace drag sail of its kind for the multiple accelerated return of retired satellites. The idea behind it: „Just keep space „cleangreen“ by launching only what you have equipped with a device to bring it quickly back home after use“, says Ernst K. Pfeiffer, CEO of German spacetech company HPS. ADEO is available from HPS in different versions tailored to the size and weight of the spacecraft in question. In this case, it is one of the smallest versions, weighing just 800 grams, with dimensions of only 10x10x10 centimeters and a sail area of 3.6 square meters.
HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer is convinced that ADEO came at exactly the right time to promote sustainable NewSpace development by avoiding the threat of apocalyptic space debris scenarios, despite rapidly growing constellations. In this context, Pfeiffer emphasizes the excellent R&D support provided by engineers and test facilities of the DLR Institute of Space Systems in Bremen, as well as the various economic development support contracts and grants provided by ESA, DLR and the Free State of Bavaria.
The implementation of the technology developed by HPS’s NewSpace Team at Munich headquarters was largely supported by the hands of engineers and technicians of the Romanian subsidiary and Romanian workshops. This is now, according to Pfeiffer, „our clear advantage having all in one company: heritage from institutional space, a tailored „internal start-up department“, a steadily growing house in Bucharest and several trustful development and production partners. New and expanded challenges to innovation and manufacturing are already waiting.“
At the end of the nominal ION-mission, in front of its “eyes” of the integrated cameras, the ADEO braking sail module unfolds, shows its „wings“ and leads ION to residue-free disposal by incineration in the atmosphere much quicker than without the sail. The first 100 km of descent will be monitored intensively. This is planned to happen in a mission slot between December ´21 and January ´22. This mission now is the last verification in a series that also encompasses a first flight on Rocket Lab´s Electron in 2018 and several parabolic flights until 2021.
With this inflight-proof of maturity ADEO is targeted to go then into serial production for customers already waiting in the U.S., Europe and Asia.


May 2021
After 6 years of development, including a zero-G parabolic campaign and a first test flight end 2018 with Rocket Lab’s ELECTRON, HPS signed on 30.04.2021 the contract with D-Orbit for the flight of the ADEO-N, named „Show me your Wings“, on the space logistics company’s orbital tranportation vehicle ION Satellite Carrier. The launch of the „Wild Ride“ Mission will take place already summer this year from a launch site in USA.
ADEO, the world’s only industrial NewSpace drag sail of its kind for the multiple accelerated return of retired satellites, is available from HPS in different versions tailored to the size and weight of the spacecraft in question. In this case, it is one of the smallest versions, weighing less than one kilogram, with dimensions of only 10x10x10 centimeters and a sail area of 3.6 square meters. It has been integrated directly into the ION platform at D-Obit now, mid May. ION is a space vehicle that can transport satellites in orbit and release them individually into distinct orbital slots. At the end of the nominal ION-mission, in front of its “eyes” of the integrated cameras, the ADEO braking sail module unfolds, shows its „wings“ and leads ION to residue-free disposal by incineration in the atmosphere much quicker than without the sail. The first 100 km of descent will be monitored intensively.
HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer is convinced that ADEO came at exactly the right time to promote sustainable NewSpace development by avoiding the threat of apocalyptic space debris scenarios, despite rapidly growing constellations. In this context, Pfeiffer emphasizes the excellent R&D support provided by engineers and test facilities of the DLR Institute of Space Systems in Bremen, as well as the various economic development support contracts and grants provided by ESA, DLR and the Free State of Bavaria.
The implementation of the technology developed by HPS’s NewSpace Team at Munich headquarters was largely supported by the hands of engineers and technicians of the Romanian subsidiary and Romanian workshops. This is now, according to Pfeiffer, our clear advantage having all in one company: heritage from institutional space, a tailored „internal start-up department“, a steadily growing house in Bucharest and several trustful development and production partners. New and expanded challenges to innovation and manufacturing are already waiting.
According to Renato Panesi, co-founder and CCO of D-Orbit: „We are very happy to have a chance to work with HPS on this project: sustainability in general has always been a relevant aspect of our identity, and with HPS we share a common vision aiming to a sustainable access to space. Being able to help HPS to test a new and innovative technology like ADEO to help control the increment of space debris is a point of pride for us. To HPS is reserved the grand finale of the mission and, while we are going to „enjoy the ride“, we are really looking forward to it“.
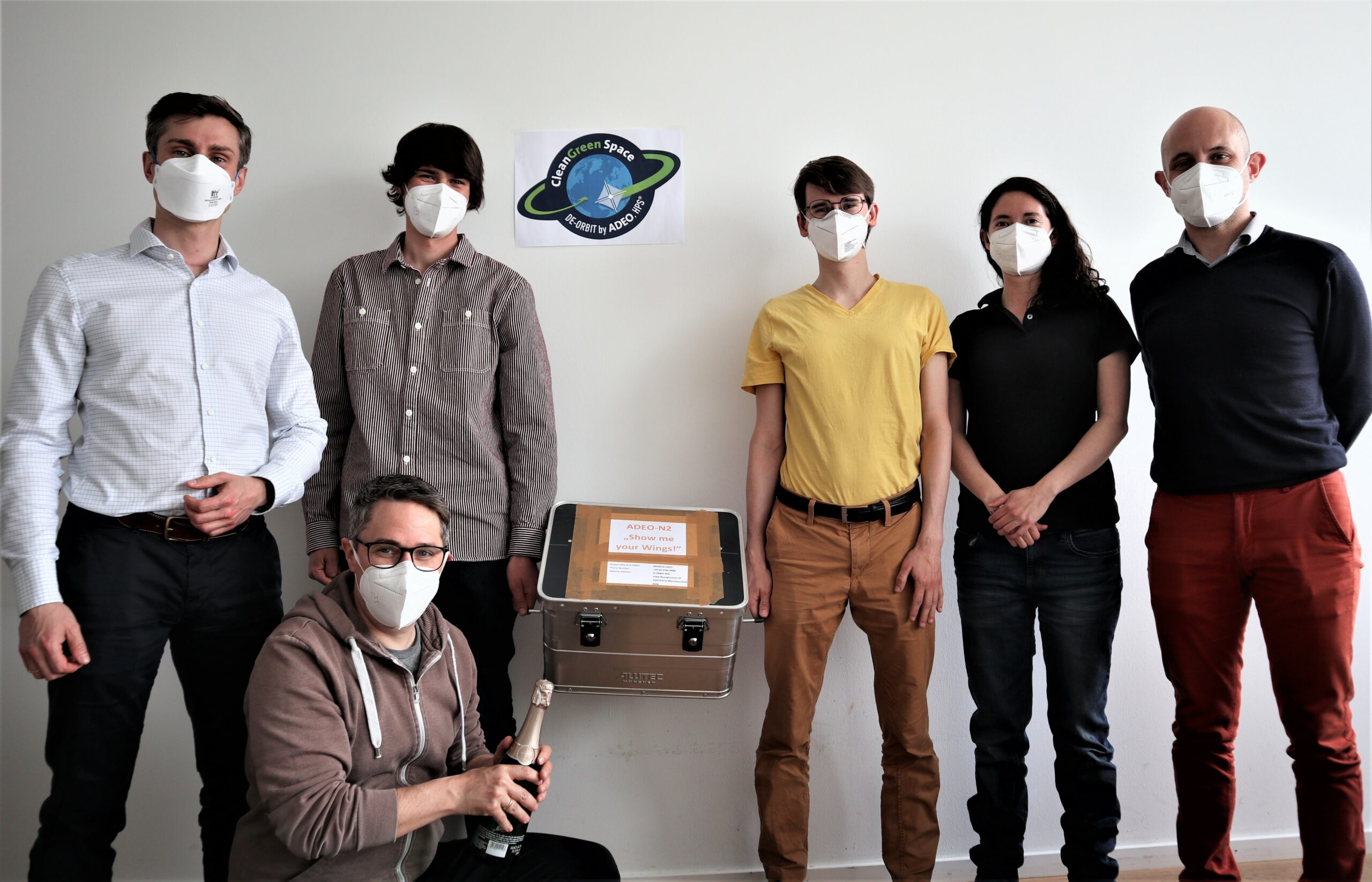
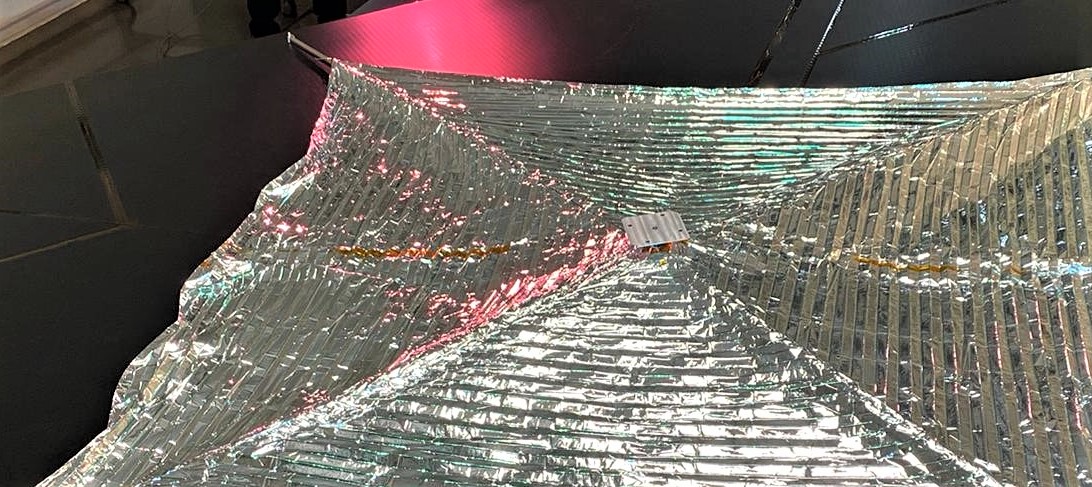


March 2016
Hardly any messages have dominated the space community´s discussions in the past two years as perseverently as these two:
So, on the one hand enormous growth of the satellite business is to be foreseen, on the other hand this business needs better rules in order to be sustainable. „Clean Space“ is ESA´s answer in general and the quest for a new, fully ecological de-orbiting sailsystem in particular.
While currently satellite manufacturers are already facing problems to comply with the 25-years-deorbiting „guideline“ without minimising the effectiveness and increasing the cost of their missions, ESA now aims to make this period as a strict requirement leaving neither ecological nor economical footprints.
Capitalizing on previous research and development in this area like the precursor project ADEO, led by the subsystem prime HPS with its consortium of DLR-institutes in Bremen and Braunschweig and the SMEs Etamax and HTS, ESA now announced its expectations for a full fledged demonstrator ready to fly by 2018 with a deorbiting time of lower than 5 years. The new project will be ignited this year and ESA´s subsystem prime HPS is expected to take this next step towards the final breakthrough in deorbiting technology, too, because:
HPS as ESA subsystem prime is aiming at the follow-on project also with its proven partners.
In parallel and as leading specialist on deployable structures and antennas, HPS Germany acts as prime contractor for Large Deployable Antennas (LDA) in cooperation with the German SME LSS, while the HPS subsidiary in Portugal is working on a deployable highprecision mast system (10-20m) for instruments weighing 100-250 kg on science missions.


June 2016
Space-News:
In den letzten Wochen und Monaten haben Sie als Sprecher der deutschen Raumfahrt-KMU einen Marathon der Veranstaltungen in Vorbereitung der ESA-Ministerratskonferenz absolviert. Kam diese plötzliche Berücksichtigung der Raumfahrt-KMU durch die Institutionen für Sie überraschend?
Pfeiffer:
Keineswegs. Zum einen haben wir in den vergangenen Jahren sehr stark drauf hingearbeitet, dass unser AKRK-Zusammenschluss der rund 40 von insgesamt 90 Raumfahrt-KMU mit ca. 1500 von insgesamt 2500 Beschäftigten in Deutschland endlich als einziger unabhängiger Ansprechpartner des Mittelstandes zur Kenntnis genommen wird. Und sicher hat auch unsere kumulierte Darstellung von Kompetenz, Wirtschafts- und Innovationskraft in der kürzlich vorgestellten Website „Best-of-Space.de“ dazu beigetragen. Wir sind in der Tat auf Augenhöhe mit den Großen der Branche von ESA und deutschem Wirtschaftsministerium berücksichtigt worden. Das galt zwar schon zum High Level Forum der ESA im Juni letzten Jahres, startete aber dieses Jahr intensiv mit einem Vortrag über das Technologieprogramm vor den ESA-Delegierten am 9. Mai, ging über ein Top Level Gespräch über die ESA Strategie zwischen ca. 10 CEOs der europäischen Raumfahrtfirmen und ESA-Generaldirektor Herrn Wörner mit allen seinen Direktoratschefs am 12. Mai, weiter zur Panelveranstaltung „New Space“ am 2. Juni auf den Space Days der ILA in Berlin und schließlich zum diesjährigen High Level Forum der ESA am 20. Juni auf dem ich im Panel über „Next Steps for ESA“ eingeladen bin.
Space-News:
Alle reden von „new space“ ….
Pfeiffer:
Genau, alle reden über „new space“ – und meinen in Ermangelung eines europäischen Weges den amerikanischen, der da lautet: „machen, was finanzkräftige Quellen haben wollen“ und „mit privatem Risiko finanzieren, und wenn es schief geht werde ich auch nicht arm woran man selber glaubt“
„Masse über Klasse stellen und dabei Qualitätsverluste in Kauf nehmen, solange sie sich zumindest kurzfristig rechnen“.
Space-News:
Ist das auch der europäische Weg?
Pfeiffer:
Niemand in Europa wird das unterschreiben. Zum einen, weil es diese finanzkräftigen Unternehmen in D und EU nicht gibt, ebenso wenig wie die Risikofinanzierer und schon gar nicht die Mentalität, nicht nachhaltiges Billiges zu bauen, dabei Qualität zu opfern und Folgekosten (Schrott etc) für kommende Generationen ohne Ansicht der Dimension in Kauf zu nehmen.
Abgesehen davon, ist es ein gewaltiges Risiko, sich darauf zu verlassen, dass schon genügend reiche Unternehmen aus den USA auf Ideen kommen, wie sie denn durchgehend die Raumfahrtindustrie in Europa beschäftigt halten können.
Space-News:
New Space in diesem amerikanischen Sinne ist also weder europäisch, noch ist es geeignet, gerade KMU eine Perspektive zu geben?
Pfeiffer:
New Space europäischer Machart wäre das Ergebnis auch europäischen Vorgehens und Denkens. Und da haben wir eine Menge aufzuweisen. Wir machen nicht einfach mal eben so etwas, weil es vielleicht hier oder da kurzfristig Gewinn bringt – wir machen überhaupt nichts nur nach dem reinen Prinzip kurzfristigen ökonomischen Gewinns. Wir machen die Dinge in Europa so wie wir sie machen, weil für uns hier die Dinge immer einen viel tieferen Sinn und Nachhaltigkeit, als kurzfristig in Dollar messbar ergeben müssen. Ziel in Europa war es bisher, nicht nur eine Handvoll reicher Unternehmen noch reicher zu machen, sondern möglichst viele Unternehmen nachhaltig und langfristig zum Wohle einer unabhängigen, ausgeglichenen Gesellschaft zu erhalten. Derzeit besteht
Gefahr, dass dieses Gleichgewicht und die Unabhängigkeit in Europa kippt.
Space-News:
Wie drückt sich das aus?
Pfeiffer:
Lassen Sie mich ein Bild bemühen. Nach eben beschriebener amerikanischer Mentalität soll ein Produkt hinreichend funktionieren, nur Schäden für den unmittelbaren Nutzer müssen ausgeschlossen bleiben. Auch wir können uns sicher nicht alle der Faszination eines mächtigen V8 und dem Reiz vergleichsweise unendlichen Sitz- und Reisekomforts eines typischen US-Autos entziehen. Im Gegensatz zum Amerikaner nehmen wir es dann aber schon übel, wenn zugunsten eines schnelleren Verkauf garantierenden Preises dann unterwegs mal ein Knopf hier abfällt oder ein Schalter da nicht funktioniert. Und erst recht unakzeptabel ist für uns die Vorstellung von ressourcenvernichtenden Trinksitten und materialverschwendendem Design, was alles dann nur nachfolgenden Generationen Probleme macht. In Europa denken wir anders; Nachhaltigkeit hat für uns zwingend etwas mit Qualität zu tun. Darin sind wir gut, und darin sind wir besser als alle anderen – USA, Asien, Russland.
Space-News:
Was folgt daraus für „new space“ made in Europe?
Pfeiffer:
Wenn das so ist, sollten wir das auch zur Grundlage unseres „European way of new space“ machen. Nicht warten, bis irgendwer von irgendwo irgendeinen kommerziellen Auftrag platziert, sondern die Landschaft solcher Aufträge samt Staat, Auftraggebern, Programmen und Auftragnehmern selbst vorzeichnen.
Wenn wir als KMU politik- und öffentlichkeitswirksam dieses Feld der systematischen Suche nach vernünftigen, nachhaltigen und politisch wie wirtschaftlich höchst wünschenswerten „new space – Projekten made in Europe“ besetzen, besetzen wir damit gleich das ganze Feld „new space“ selbst und jegliche Diskussion darum. Wir stellen solide Weichen, statt blind Trittbrett zu fahren!
Space-News:
Kann das wirklich in Anbetracht der „unendlichen Möglichkeiten“ jenseits des Atlantiks funktionieren?
Pfeiffer:
Sicher kann es das, und ich bin darüber hinaus sicher, dass es seine Wirkung auf den „American way of new space“ auch nicht verfehlen wird. Nehmen Sie wieder das Bild vom Auto. Wie kommt es wohl, dass amerikanische wie auch japanische Hersteller in den letzten rund zwanzig Jahren vermehrt dazu übergehen, europäisches Design, und europäische Technik und Europäisches Umweltbewußtsein als Maßstab mitzunutzen? Das Bessere ist des Guten Feind, das wird auch bei „new space“ auf lange Sicht nicht anders sein.
Space-News:
Ist das Ihre Hauptbotschaft auf dem Marathon zur Ministerratskonferenz?
Pfeiffer:
Das und der dringende Hinweis, dass wir beim Hype um „new space“ unseren „old space“ nicht vergessen sollten, sprich: weiterhin Investition in Höchst-Technologie. Gerade wir Deutschen sind ja oftmals so eifrig dabei, neue Dinge – besonders, wenn sie aus den USA kommen – über das Bestehende zu stellen. Davor kann ich nur warnen. Bei aller Begeisterung für Neues – die liegt ja auch irgendwo in der menschlichen Natur – das zu vernachlässigen, was uns in der Raumfahrt groß gemacht hat, endet für uns im Desaster, in einer verlorenen Unabhängigkeit Deutschlands. Um abschließend noch mal den Autofahrer-Blick einzunehmen: Wenn wir mit unausgegorener Taktik, mangelnder Schnelligkeit und unzureichender (Finanz-) Kraft auf die linke Spur wechseln, um einer Chimäre nachzujagen, müssen wir uns nicht wundern, wenn uns traditionelle, staatsgetriebene Old-Space-Länder Europas und Asiens auf der Pannenspur technologisch überholen. Als Raumfahrt-KMU werden wir jedenfalls schön weiter hochinnovativ die technologische Mitte besetzen und von dort aus versuchen, flexibel mit neuen, kreativen Ideen von Anwender-KMU den „European Way of New Space“ zu leben.
Eine zweite Botschaft an die Ministerratskonferenz wäre noch: Nutzt die aktuelle Begeisterung für Raumfahrt in der Gesellschaft für Inspiration, europäischen Zusammenhalt, globale Zusammenarbeit und damit Friedenssicherung.
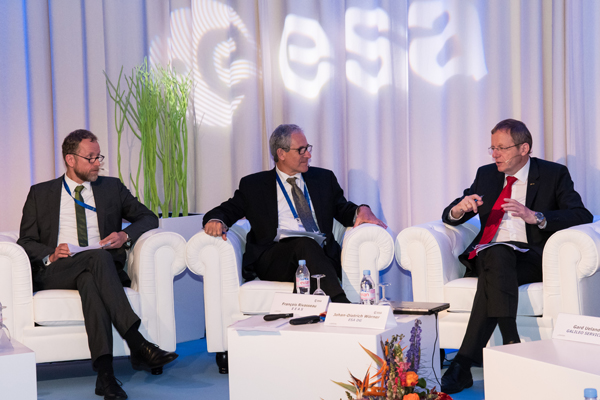





June 2018
Just a few weeks before the launch of „Pride of Bavaria“, the space test mission of the nano-version of the space sail system ADEO for fast deorbit of decommissioned satellites, Bavarian minister of economy Franz-Josef Pschierer paid a personal visit to HPS, the Munich based driver of spacetech innovations. Founder and CEO of HPS, Dr. Ernst K. Pfeiffer, explained the ADEO-system designed to avoid space debris – a unique development which has been funded by Bavaria – and also introduced other important product lines to the minister: reflectors for antennas serving earth observation and telecommunications projects in space, which today are the European benchmark in high frequency data transmission, thermal and radiation protection systems, large deployable antennas, and a high-precision mesh-net for the reflection of antenna signals – developed by HPS and produced in Hof, center of the Bavarian industrial „textil triangle“. (Links to tv-coverage/interviews: https://www.sat1.de/regional/bayern/videos/die-sendung-vom-25-05-2018-ganze-folge)
On Saturday, May 26th, the HPS-crew took the ADEO flight model plus a spare to the launch site in New Zealand. ADEO will be launched end of June aboard an American ELECTRON rocket of RocketLab (lLinks: http://spacenews.com/rocket-lab-reschedules-next-electron-launch/; https://www.rocketlabusa.com/)
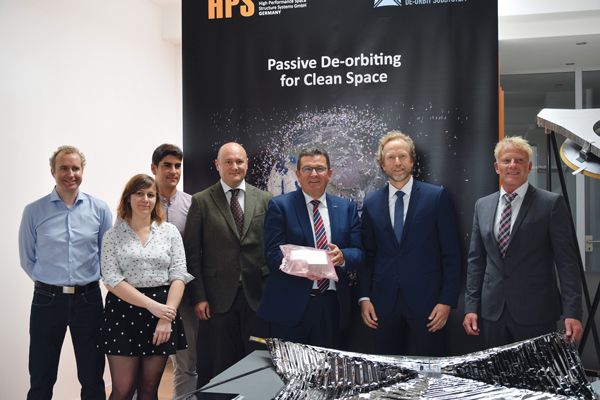
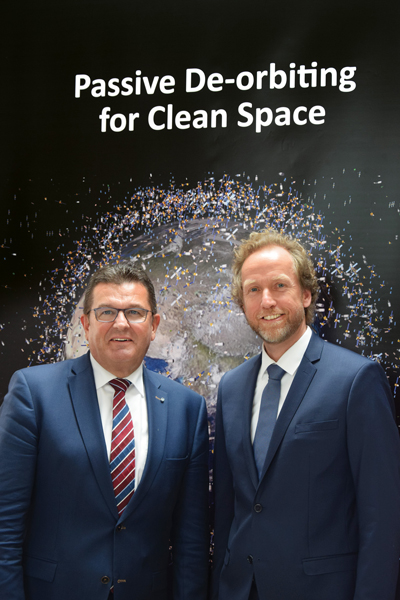


November 2018
On the 11th of November at 4:50am Central European Time, the HPS GmbH developed NABEO-1 dragsail technology demonstrator was launched into space onboard the Rocket Lab Electron rocket #ItsBusinessTime. This dragsail is a means to passively remove satellites from highly congested Low Earth Orbit regions after their mission life without the need for the spacecraft to be still alive.
With a dragsail area of 2.5m2 deployed from a cubesat sized box (<1U: 10cm x 10cm x 10cm) the NABEO-1 dragsails fit right into the ADEO-N dragsail class for cube and nanosatellites. Further developments for dragsails for larger missions (ADEO-L for 100-500kg satellites) are currently undertaken at the ESA GSTP/CleanSpace activity ADEO which will lead to a qualified dragsail Protoflight Model in 2020 with a follow up In-Orbit Demonstration Mission right after.

The opportunity to fly the NABEO technology demonstrator on the #ItsBusinessTime mission was offered by Rocket Lab (Huntington Beach, CA, USA / Auckland, New Zealand) and Ecliptic Enterprises Corporation (Pasadena, CA, USA) via Ecliptic’s Hosted Payload Program (HPP), with NABEO-1 serving as a pathfinder for demonstrating the Electron rocket’s hosted payload capabilities. The NABEO-1 subsystem development at HPS GmbH was co-funded by the Bavarian Ministry of Economic Affairs, Energy and Technology. The foundations for the dragsail technology have been laid in 2017 by joint research activities between the DLR Institute for Space Systems (Bremen), Fraunhofer Ernst Mach Institute (Freiburg), and HPS GmbH (Munich).
The #ItsBusinessTime rocket was launched from Rocket Lab’s Launch Complex 1 at the Mahia Peninsula on the North Island of New Zealand. The NABEO-1 subsystem was attached to the kick stage (3rd stage) of the Electron rocket and stays on the kick stage for its deployment which was commanded 2 hours intro the flight. Currently, the team at HPS GmbH is waiting for a confirmation of the dragsail deployment with the help of the Falcon Telescope Network who will also try to investigate the de-orbit behavior of the kick-stage with the attached dragsail via their optical telescopes.