CIMR-LDRS: The lighthouse project for non-dependence in European space travel enters the production phase of the qualification model (EQM) as planned
April 2025

CIMR-LDRS: The lighthouse project for non-dependence in European space travel enters the production phase of the qualification model (EQM) as planned
April 2025
Long before an unspeakable bloodbath sealed the end of peaceful life in Eastern Europe in 2022, the demand for technological “non-dependence” had already conquered a top position among the strategic priorities in German and European space travel. The focus was particularly on large reflector antennas that could be deployed in space, suitable for missions of all kinds.
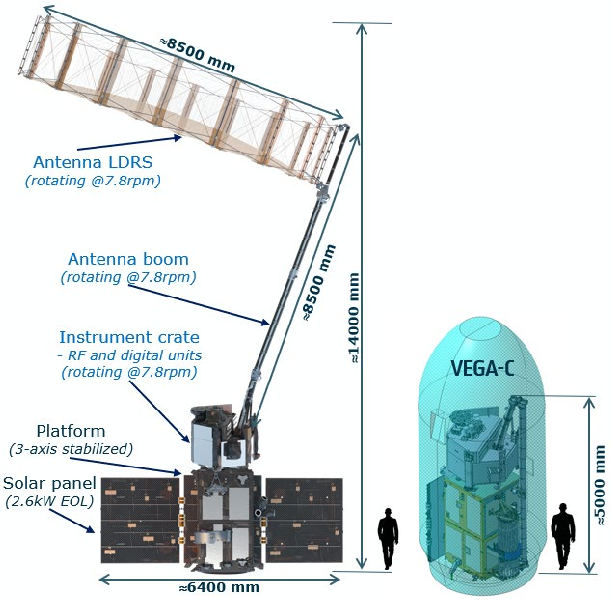
The history of this German technology for Europe began more than a decade ago with SCALABE, a technology development funded by ESA, and SMERALDA (SME’s Radar and Large Deployable Antenna), a study funded by the German Space Agency with significant participation by antenna specialist HPS GmbH. Through further technical chapters of successful concretization of the goal with significant support from ESA and the EU, the Munich-based company finally led a consortium of mostly medium-sized partners from eight countries to the spectacular win of the 115 million euro contract from Prime`sThalesAlenia Space (TAS) for “CIMR LDRS” (Large Deployable Reflector Subsystem) in 2020: the world’s largest rotating deployable reflector antenna construction for the EU’s Copernicus Imaging Microwave Radiometer (CIMR) lighthouse project for observing land, ice and oceans, particularly the Arctic, from space under the management of the European Space Agency (ESA). The LDR subsystem consists of a reflector, arm, deconvolution electronics, cabling, various hold-down mechanisms and thermal hardware.
After a long design phase and intensive iteration with the direct customer TAS in Rome and the end customer ESA, the go-ahead was given in phase C/D with the completion of the first so-called “Manufacturing Readiness Review” for the construction and testing of a qualification model (Engineering Qualification Model, EQM). In these days of spring 2025, HPS has now finally entered the intensive phase of manufacturing the EQM.
Challenges on the way to new shores
The technical challenges were and are immense, as the goal is nothing less than a deployable reflector construct for high frequencies (Ka-band) with a diameter of eight meters on an equally deployable eight-meter-long arm that rotates around its own axis eight times per minute in orbit. This results in extreme requirements such as an RMS (Root Mean Square) value for the surface accuracy, which must be much smaller than 1/10 mm over the entire 50 m² reflector surface, or a maximum permissible deviation of the 8 m distant arm tip of just 10 mm from the nominal value, including vibrations, centrifugal force and thermal deformations.
The challenges of managing the various aspects of the project were and are no less demanding. The program management of the CIMR team from ESA and TAS has played a prominent role from the outset, while HPS GmbH, known for its heritage in institutional, military and commercial antenna construction – in addition to its own development work at arm and subsystem level – is responsible for managing the consortium of around a dozen SMEs, including such outstanding innovation drivers as Munich-based LSS GmbH for the deployable reflector assembly (DRA), based on a highly successful, long-standing development partnership. The lightweight carbon struts for the DRA come from the former Portuguese HPS subsidiary and now FHP, INVENT GmbH contributes the carbon fiber-reinforced tubes for the 8-meter deployable support arm (DAA), NanoSpace Switzerland develops and produces the high-precision yet stable, motor-driven joints of the arm, HPS Romania and INEGI Portugal the constructions for ground tests and transports (“MGSE”). In addition, HPS is responsible for providing the central element for the deployable reflector: the measurably best Ka-band MESH from HPtex that is available to buy in a 9m x 9m size – and, as a “made in Germany” product, transforms European non-dependence from vision to reality. Until then, a MESH in such dimensions had only been available in American production. Originally planned as an essential element of the German-European supply chain for CIMR, the joint venture HPTex GmbH (JV of Iprotex GmbH & Co. KG and HPS GmbH), founded in 2020, now sells its mesh products worldwide, especially in Asian and continental American countries. The EQM mesh for CIMR recently came out of HPtex production.
The most important components (DAA and DRA) will be ready by the end of the year, and the series of tests will begin early in 2026.
“If you want to be ahead, you shouldn’t be afraid of the unknown” (Ernst K. Pfeiffer)
When CIMR sets off on its mission in 2029 on board a Vega C in a sun-synchronous orbit to observe ice sheets and snow, among other things, from dawn to dusk, Europe will not only benefit from the knowledge gained from the project, but also from the certainty of having mastered the step towards technological LDRS independence. LDRS are also products for a range of military applications that can contribute to an increased defense capability, especially in these years. HPS CEO Ernst K. Pfeiffer sees this as a milestone that goes far beyond the immediate success of the project: “This space project is clear proof that the mentality of all those involved in the project – both industry and institutions – is completely different to the risk aversion that the public normally attributes to Germany in particular, and to some extent also to ESA. Not being afraid of the unknown is the first key to success. Way up front is where it´s getting dark. Especially in space. But not only there.”